Identification of Crucial Genes Associated With MYCN-Driven Neuroblastoma Based on Single-Cell Analysis and Machine Learning
- PMID: 40600620
- PMCID: PMC12216506
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.71008
Identification of Crucial Genes Associated With MYCN-Driven Neuroblastoma Based on Single-Cell Analysis and Machine Learning
Abstract
Background: Neuroblastoma (NB) with MYCN amplification is strongly correlated with high-risk stratification and poor prognosis. However, the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Elucidating these pathways is critical for advancing personalized treatments for MYCN-driven NB.
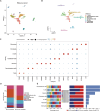
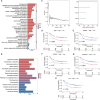
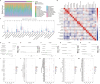
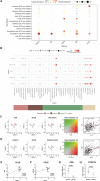
Methods: We performed single-cell transcriptomic analysis comparing NB samples with and without MYCN. Key genes were then identified using machine learning based random survival forest (RSF) and nomogram analyses. The influence of key genes on immune infiltration and molecular mechanisms driving NB progression were further investigated. Finally, we visualized the expression levels and global function of these genes in single-cell datasets and validated their expression in patient samples through RT-qPCR.
Results: Single-cell transcriptome analysis of GSE218450 identified marker genes specific to NB cells. RSF and nomogram analyses revealed that overexpression of CKB, PCSK1N, OTUB1, and VGF is associated with poor prognosis, whereas upregulation of NTRK3 indicates a favorable prognosis. These genes are significantly associated with immune cell infiltration and play an important role in modulating the immune microenvironment. Pathway analysis further showed that these genes influence critical signaling pathways, including the Wnt pathway, and interact with tumor-related genes. Additionally, we confirmed that CKB and PCSK1N are positively correlated with MYCN in NB cell lines and are significantly overexpressed in MYCN-amplified NB patients.
Conclusions: Our results provide molecular insights into the transcriptional changes associated with MYCN amplification in NB. In particular, the identification of CKB and PCSK1N suggests their potential role in driving tumor progression, making them promising targets for novel treatments in MYCN-driven NB.
Keywords: MYCN amplification; neuroblastoma; nomogram model; random survival forests; single‐cell transcriptome.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gomez R. L., Ibragimova S., Ramachandran R., Philpott A., and Ali F. R., “Tumoral Heterogeneity in Neuroblastoma,” Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. Reviews on Cancer 1877, no. 6 (2022): 188805. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

