Human eIF2A has a minimal role in translation initiation and in uORF-mediated translational control in HeLa cells
- PMID: 40600802
- PMCID: PMC12221301
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.105311
Human eIF2A has a minimal role in translation initiation and in uORF-mediated translational control in HeLa cells
Abstract
Translation initiation in eukaryotes requires a 40 S ribosome loaded with initiator tRNA which scans for an initiation codon. The initiator tRNA is usually recruited to the ribosome as part of a ternary complex composed of initiator tRNA, eIF2, and GTP. Although initiator tRNA recruitment was originally ascribed to another factor, eIF2A, it was later disproven and shown to occur via eIF2. Nonetheless, eIF2A is still considered a translation initiation factor because it binds the ribosome and shows genetic interactions with other initiation factors such as eIF4E. The exact function of eIF2A during translation initiation, however, remains unclear. Here, we use ribosome profiling and luciferase reporter assays to systematically test in HeLa cells the role of eIF2A in translation initiation, including translation of upstream ORFs. Since eIF2A is thought to take over the function of eIF2 when eIF2 is inhibited, we also test conditions where the integrated stress response is activated. In none of our assays, however, could we detect a role of eIF2A in translation initiation. It is possible that eIF2A plays a role in translation regulation in specific conditions that we have not tested here, or that it plays a role in a different aspect of RNA biology.
Keywords: biochemistry; chemical biology; developmental biology; eIF2; eIF2A; human; translation.
© 2025, Roiuk et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MR, MN, AT No competing interests declared
Figures
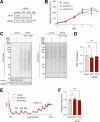
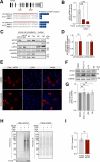
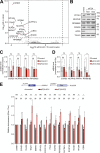
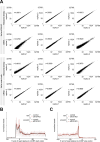
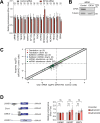
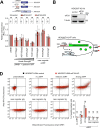
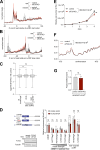
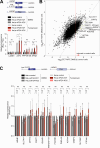
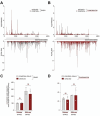
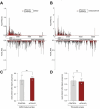
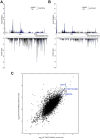
Update of
References
-
- Anderson R, Agarwal A, Ghosh A, Guan BJ, Casteel J, Dvorina N, Baldwin WM, Mazumder B, Nazarko TY, Merrick WC, Buchner DA, Hatzoglou M, Kondratov RV, Komar AA. eIF2A-knockout mice reveal decreased life span and metabolic syndrome. FASEB Journal. 2021;35:e21990. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101105R. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

