Mediator Kinase Inhibitor Selectivity and Activity in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 40601435
- PMCID: PMC12281475
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5c00338
Mediator Kinase Inhibitor Selectivity and Activity in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
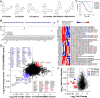
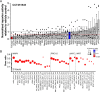
The Mediator complex is a regulator of gene expression, influencing chromatin structure and RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription. Its activity is controlled by a protein kinase module, which includes cyclin-dependent kinases 8 and 19, that phosphorylates RNA polymerase II and transcription factors to regulate gene expression. Using orthogonal approaches combining chemical and genetic tools, we demonstrated the selectivity of our small-molecule inhibitors derived from 3,4,5-trisubstituted pyridine and 3-methyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine chemical series in human colorectal cell culture and tumor xenograft models. The lack of activity of our inhibitors in CDK8/19 double knockout models, with respect to molecular, proliferative, and antitumor end points, revealed their specificity and dependence on these kinases. Using our chemical probes and knockout models, we explored Mediator kinase function in human colorectal cancer cells. Phospho-proteome profiling revealed substrates enriched with transcription and chromatin regulators, while promoter reporter experiments identified transcription factor binding sites, including TCF/LEF and AP1, regulated by Mediator kinases. Additionally, altered phosphorylation of several Mediator subunits suggests a mechanism for the rapid regulation of the Mediator complex. Overall, our results demonstrate that CDK8 and CDK19 play pivotal roles in regulating gene expression associated with oncogene activation and signaling pathways. Further studies are warranted to elucidate their broader cellular roles and regulatory mechanisms. The selective inhibitors validated in this study will provide valuable tools for such mechanistic investigations into Mediator kinase functions and their potential therapeutic exploitation.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

