Measles vaccines and non-specific effects on mortality or morbidity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40601595
- PMCID: PMC12221017
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321982
Measles vaccines and non-specific effects on mortality or morbidity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: This review evaluates the hypothesis of beneficial non-specific effects of the standard-titre measles vaccine.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Trials included standard or high-titre live attenuated measles containing vaccines compared to other vaccines or placebo. The primary outcomes were mortality and morbidity. Secondary outcomes were infections, antibiotic use, atopy, allergies, asthma, and atopic dermatitis.
Findings: 23 articles were included in this systematic review. Mortality: Two doses of measles vaccine vs. only one dose showed no significant effect on mortality; risk ratio (RR) = 1.05 (95% CI: 0.78 to 1.41), p = 0.76. The analysis was based on a relative risk reduction (RRR) of 25% and a control group event rate of 2.32% as measured in the actual trials included in the analysis. In males, the association was rejected: RR = 1.09 (0.86 to 1.37), p = 0.47. In females, the association was not rejected at 25%,but was at 33% level: RR = 1.0 (0.64 to 1.54), p = 0.99. Morbidity: Overall, the hypothesis was rejected: RR = 0.94 (0.80 to 1.10), p = 0.43. The rejection was sustained for both sexes: females RR = 0.95 (0.77 to 1.18), p = 0.6; males RR = 0.92 (0.83 to 1.03), p = 0.13.
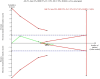
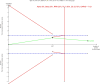
Interpretation: Based on evidence from randomised controlled trials, this systematic literature review and meta-analysis did not support the hypothesis of non-specific effects of standard-titre measles containing vaccines. Trial Sequential Analysis indicated that the meta-analysis included sufficient data to reach this conclusion.
Trial registration: PROSPERO CRD42022344473.
Copyright: © 2025 Fournais et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Direct-acting antivirals for chronic hepatitis C.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9(9):CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28922704 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Direct-acting antivirals for chronic hepatitis C.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 6;6(6):CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9:CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub3. PMID: 28585310 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention C. Measles epidemiology. https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/newsroom/topics/measles/index.html. 2019. Accessed 2024 January 1
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

