PLZF promotes compensatory lung growth by increasing HPMEC proliferation and angiogenesis
- PMID: 40601668
- PMCID: PMC12221005
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325936
PLZF promotes compensatory lung growth by increasing HPMEC proliferation and angiogenesis
Abstract
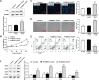
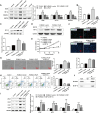
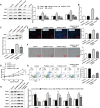
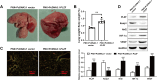
Angiogenic signaling pathway activation has been shown to accelerate compensatory lung growth (CLG) after unilateral pneumonectomy (PNX). Therefore, studying specific genes regulating angiogenic signaling pathways is a novel strategy to promote CLG. EdU, flow cytometry and tube formation experiments were performed to test the metabolism of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMECs). Western blotting was used to analyze the levels of promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein (PLZF), kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), hemeoxygenase-1 (HO-1), quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1), nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and other proteins. The proliferation of pulmonary endothelial cells was assessed by Ki67 double staining. A unilateral PNX mouse model was constructed, and changes in lung volume and weight were assessed. Our bioinformatics results suggested that PLZF showed a clear downward trend after unilateral PNX. PLZF overexpression significantly promoted HPMECs proliferation and angiogenesis and inhibited their apoptosis. Further studies revealed that both Keap1 overexpression and Nrf2 silencing altered the effects of PLZF overexpression on HPMECs and inhibited their apoptosis. Notably, HIF-1α silencing reversed the effect of PLZF overexpression on HPMECs angiogenesis but not on proliferation or apoptosis. Knockdown of Nrf2 not only affected HPMECs proliferation and apoptosis but also affected angiogenesis. An in vivo study confirmed that PLZF overexpression promoted an increase in residual lung volume and lung weight in mice after unilateral PNX and significantly promoted the proliferation of lung endothelial cells. In conclusion, our study revealed that PLZF promotes HPMECs proliferation and angiogenesis and accelerates CLG by inhibiting Keap1 activation of the Nrf2 and HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathways.
Copyright: © 2025 Peng et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Buyang Huanwu Decoction promotes angiogenesis after oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury of bEnd.3 cells by regulating YAP1/HIF-1α signaling pathway via caveolin-1].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 Jul;50(14):3847-3856. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250213.705. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40904071 Chinese.
-
MiR-143-5p regulates the proangiogenic potential of human dental pulp stem cells by targeting HIF-1α/RORA under hypoxia: A laboratory investigation in pulp regeneration.Int Endod J. 2024 Dec;57(12):1802-1818. doi: 10.1111/iej.14133. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Int Endod J. 2024. PMID: 39126298
-
TRIM34-Mediated Ubiquitination and Degradation of HIF-1A Regulates Glycolysis in Endothelial Cells, Inhibits Angiogenesis, and Relieves the Progression of Lung Fibrosis.J Gene Med. 2025 Aug;27(8):e70032. doi: 10.1002/jgm.70032. J Gene Med. 2025. PMID: 40836270
-
Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 on vascular endothelial growth factor expression in exercised human skeletal muscle: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025 Jul 1;329(1):C272-C282. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00297.2025. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40522862 Review.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha in lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016 Jun;36(3):321-327. doi: 10.1007/s11596-016-1586-7. Epub 2016 Jul 5. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27376798
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

