Development and field application of metabarcoding-adapted mt-ND4 markers shows substantial gene flow and varying local pressures on Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta populations in the UK
- PMID: 40601687
- PMCID: PMC12221061
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327254
Development and field application of metabarcoding-adapted mt-ND4 markers shows substantial gene flow and varying local pressures on Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta populations in the UK
Abstract
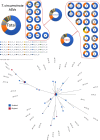
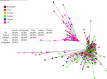
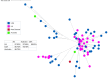
Gastrointestinal nematodes impose a significant burden on livestock production and public health by reducing animal productivity and increasing the environmental impact of farming. Modern sequencing techniques enable the efficient exploration of genetic diversity, necessary to inform effective parasite control. In this study, we developed and validated new mitochondrial ND4-based markers adapted for high-throughput sequencing. This enabled detailed analysis of genetic diversity in two important nematode species, Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta. Laboratory validations confirmed that the assay reliably detected as little as 1% of larvae in mixed samples and accurately identified strain variants. Field application on 30 sheep farms across England and Scotland revealed 60 unique genetic variants in H. contortus and 35 in T. circumcincta. A single variant dominated the sequence reads in both species, particularly T. circumcincta. Regional comparisons showed that H. contortus exhibited fewer yet persistent variants in Scotland than in England; while phylogenetic analyses indicated a common origin and significant gene flow between regions. In contrast, T. circumcincta, despite being more prevalent across all farms, displayed lower overall diversity with a shared dominant variant; evidence of dual origins and marked regional differences in evolutionary pressures. Comparisons with publicly available global sequence data revealed distinct clustering of H. contortus isolates, separating Asian sequences from those in the United Kingdom and Australia. T. circumcincta isolates showed no apparent geographic clustering. These findings demonstrate the potential of high-throughput mitochondrial marker analysis to unravel complex parasite population dynamics, and to inform sustainable management strategies in the face of challenges such as drug resistance and climate change.
Copyright: © 2025 Zahid et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Taylor M, Coop R, Wall R. Veterinary Parasitology. 4 ed. UK: Wiley Blackwell. 2016.
-
- Vlassoff A. Seasonal incidence of infective trichostrongyle larvae on pasture: the contribution of the ewe and the role of the residual pasture infestation as sources of infection to the lamb. N.Z. J Exp Agric. 1976;4(3):281–4. doi: 10.1080/03015521.1976.10425884 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

