Social exclusion and mental health of youths affected by parental HIV/AIDS in China: Based on a serial mediating model
- PMID: 40601712
- PMCID: PMC12221013
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327089
Social exclusion and mental health of youths affected by parental HIV/AIDS in China: Based on a serial mediating model
Abstract
Methods: 297 youths affected by parental HIV/AIDS were recruited to completed questionnaires of social exclusion, perceived stress, future orientation and mental health. The bootstrap method was used to examine the mediation effects.
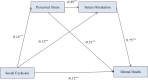
Results: It showed that: (1) the social exclusion (M = 32.48, SD = 15.25) significantly and negatively predicted the mental health (M = 93.27, SD = 19.08). (2) Perceived stress (M = 39.28, SD = 6.35) mediated the negative effect of the social exclusion and mental health. (3) Future orientation (M = 57.44, SD = 8.15) mediated the relationship between social exclusion and mental health. (4) Perceived stress and future orientation could play a chain-mediating role in the mechanism of social exclusion affecting the mental health.
Conclusions: Results of this study support the Stress and Coping Theory (SCT) and demonstrate the damaging effect of perceived stress and the protective effect of future orientation in mediating the relationship between social exclusion and mental health among youths affected by parental HIV/AIDS in China. Future mental health promotion and intervention efforts targeting these youths or other youths with early childhood adversity should include components that could mitigate the negative impact of social exclusion on their lives.
Copyright: © 2025 Wan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Interventions for improving the psychosocial well-being of children affected by HIV and AIDS.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Apr 15;2009(2):CD006733. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006733.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 19370650 Free PMC article.
-
Welfare-to-work interventions and their effects on the mental and physical health of lone parents and their children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 26;2(2):CD009820. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009820.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29480555 Free PMC article.
-
Social Stories™ to alleviate challenging behaviour and social difficulties exhibited by children with autism spectrum disorder in mainstream schools: design of a manualised training toolkit and feasibility study for a cluster randomised controlled trial with nested qualitative and cost-effectiveness components.Health Technol Assess. 2016 Jan;20(6):1-258. doi: 10.3310/hta20060. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 26792796 Free PMC article.
-
Welfare-to-work interventions and their effects on the mental and physical health of lone parents and their children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 20;8(8):CD009820. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009820.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 26;2:CD009820. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009820.pub3. PMID: 28823111 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- World Health Organization. HIV data and statistics. 2024. [Accessed 2025 May 27]. https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/s...
-
- Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Progress in HIV/AIDS prevention and control in China, 2023. 2023. http://ncaids.chinacdc.cn/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical