Design, synthesis, and biological activity of novel halogenated sulfite compounds
- PMID: 40601716
- PMCID: PMC12220988
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327587
Design, synthesis, and biological activity of novel halogenated sulfite compounds
Abstract
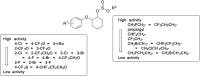
The acaricide propargite has been widely used for over 50 years without significant resistance issues. Addressing to the propargite defects of poor crop safety, thirty-six novel halogenated propargite analogues were designed, synthesized, and characterized using 1H NMR, 13C NMR spectroscopy, and HRMS. All target compounds were screened for activity against adult Tetranychus cinnabarinus (spider mites) and Myzus persicae (aphids). Two compounds exhibiting higher insecticidal activity were further evaluated for crop safety on cowpea seedlings. Structural modifications, such as replacing the tert-butyl group on the propargite benzene ring with chlorine or trifluoromethoxy, and substituting the propargyl group with fluorinated alkyl groups (e.g., 2-fluoroethyl or 3,3,3-trifluoropropyl), significantly enhanced both acaricidal and aphicidal activity. Compound 5.16 demonstrated superior acaricidal activity (LC50: 14.85 mg L-1) on Tetranychus cinnabarinus and excellent crop safety on cowpea seedlings. Additionally, Compound 5.32 exhibited both acaricidal (LC50: 14.32 mg L-1) and aphicidal activity, which is unusual in this chemical class. The compounds 5.16 and 5.32 could be used as promising leads for the discovery of novel acaricides or insecticides.
Copyright: © 2025 Liu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Jakubowska M, Dobosz R, Zawada D, Kowalska J. A review of crop protection methods against the twospotted spider mite—Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae)—with special reference to alternative methods. Agriculture. 2022;12(7):898. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12070898 - DOI
-
- Wei P, Demaeght P, De Schutter K, Grigoraki L, Labropoulou V, Riga M, et al. Overexpression of an alternative allele of carboxyl/choline esterase 4 (CCE04) of Tetranychus urticae is associated with high levels of resistance to the keto-enol acaricide spirodiclofen. Pest Manag Sci. 2020;76(3):1142–53. doi: 10.1002/ps.5627 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

