Differential Efficacy of Bevacizumab and Erlotinib in Preclinical Models of Renal Medullary Carcinoma and Fumarate Hydratase-Deficient Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 40601845
- PMCID: PMC12323885
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-24-0703
Differential Efficacy of Bevacizumab and Erlotinib in Preclinical Models of Renal Medullary Carcinoma and Fumarate Hydratase-Deficient Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
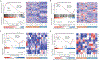
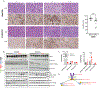
Renal medullary carcinoma (RMC) and fumarate hydratase (FH)-deficient renal cell carcinoma (RCC) are rare and highly aggressive cancers. Although the combination of VEGF inhibition by bevacizumab and EGFR inhibition by erlotinib is clinically used for both diseases, the differential effect of each component has not been investigated. Transcriptomic profiling revealed that RMC and FH-deficient tumor tissues demonstrate increased EGFR but not VEGF expression compared with adjacent normal kidney. Subsequent in vitro studies revealed that RMC and FH-deficient cell lines are sensitive to erlotinib treatment, whereas clear-cell RCC cell lines are resistant. We developed patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models of tumors exposed to first-line therapies to represent treatment-experienced RMC and FH-deficient RCC models. These models were then used to determine tumor growth response to angiogenesis inhibition by bevacizumab alone or in combination with erlotinib. The FH-deficient RCC PDX model responded to either bevacizumab or erlotinib alone or in combination, whereas the RMC PDX model responded only to erlotinib, consistent with clinical and preclinical data suggesting that RMC is refractory to angiogenesis inhibition. Statistically higher expression of EGFR was observed in the RMC PDX model compared with the FH-deficient model, whereas higher phosphorylated tyrosine-416 SRC expression was observed in the FH-deficient PDX model compared with the RMC model. Our preclinical data suggest that EGFR signaling differentially modulates tumor growth in RMC and FH-deficient RCC and that angiogenesis inhibition is a valid target in FH-deficient RCC but not RMC.
©2025 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Pavlos Msaouel has received honoraria for service on a Scientific Advisory Board for Mirati Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Exelixis; consulting for Axiom Healthcare Strategies; non-branded educational programs supported by DAVA Oncology, Exelixis and Pfizer; and research funding for clinical trials from Takeda, Bristol Myers Squibb, Mirati Therapeutics, Gateway for Cancer Research, and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Jose Karam has acted as a consultant, served on the advisory board, or has accepted an honorarium from Pfizer, Merck, Johnson and Johnson, Syapse, American Board of Urology, American Urological Association, Kidney Cancer Association, Texas Urological Society, Clarivate, Specialty Networks/MJH, Medscape, PCORI, and Guidepoint Global; he has received research funding from Roche/Genetech, Mirati, Merck and Elypta; and he owns stock in MedTek and ROM Technologies.
Figures


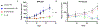
References
-
- Skala SL, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome (HLRCC): A Contemporary Review and Practical Discussion of the Differential Diagnosis for HLRCC-Associated Renal Cell Carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:1202–1215. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA288448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA096297/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA096300/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RP230271/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- RP230271/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- RP230217/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- RP230217/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- RP230217/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- RP230217/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT)
- CA096300/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- CA096297/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- MD Anderson Partnership for Careers in Cancer Science Program
- Erickson Kidney Cancer Foundation
- Eickson Kidney Cancer Foundation
- R37CA288448/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Andrew Sabin Family Foundation
- Gateway for Cancer Research (GCR)
- KC200096P1/U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- KC210213/U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- KC210213/U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- Kidney Cancer Association (KCA)
- V Foundation for Cancer Research (VFCR)
- University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (Physician-Scientist Award)
- Finneran Family Endowment
- University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (Ecksein and Alexander Laboratories)
- Chrs "CJ" Johnson Foundation
- Mike and Mary Allen
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

