Production and characterization of magnetic Biochar derived from pyrolysis of waste areca nut husk for removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater
- PMID: 40603323
- PMCID: PMC12223213
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03359-z
Production and characterization of magnetic Biochar derived from pyrolysis of waste areca nut husk for removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater
Abstract
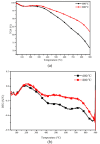
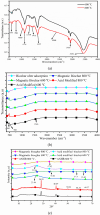
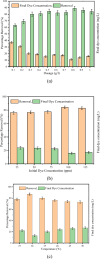
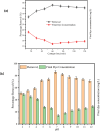
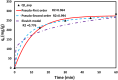
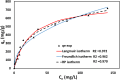
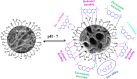
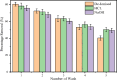
The textile industry causes lots of pollution due to its discharge of untreated coloured effluents into water bodies, impacting the environment. The present study includes a slow pyrolysis technique to produce magnetic biochar derived from waste areca nut husk (ANH)) biomass to adsorb methylene blue dye. The biochar and biomass were characterised via proximate analysis, ultimate analysis, bulk density, heating value, extractive content, biochemical analysis, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), SEM, BET surface area, pH, water holding capacity (WHC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). A semi-batch reactor was used to produce biochar (ANHB) at 600 and 800 oC at 10 oC min- 1 heating rate and 45 min holding time in an inert atmosphere. The produced biochar was magnetised by blending aqueous biochar suspensions with aqueous Fe3+/Fe2+ solutions. Further, magnetised biochar is employed to eliminate methylene blue (MB) dyes at different pHs, contact times, temperatures, dosages and concentrations. Biochar derived at 800 oC (ANHB800) gave increased carbon content (62.93%), heating value (33.02 MJ/kg), and BET surface area (112 m2/g) over biochar derived at 600 oC. The results of the acid treatment biochar (ANHBA800) demonstrated that 5M H2SO4 causes a BET surface area increase (265 m2/g) and a ash content decrease (9.96%). However, when magnetic biochar was produced at 800 oC it shows an additional increase in BET surface area upto 385 m2/g. The MB dye absorption analysis confirmed 85.47% adsorption at 0.3 g/l dosage, 100 ppm concentration, 30 oC, 60 min contact time, and pH 7. The adsorption capacity was 785.34 mg/g when fit by the Langmuir isotherm model. Magnetic nanoparticles enhance active sites, electrostatic interactions, and recovery, improving efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability in dye removal. The adsorption kinetics results suggested that the pseudo-second-order model best explains the experimental data with an R2 value of 0.994. Additionally, the adsorption isotherm studies were best fitted by the Langmuir model adsorption conforming monolayer adsorption of MB on biochar surface.
Keywords: Adsorption; Biomass; Characterisation; Magnetic Biochar; Pyrolysis; Wastewater.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Obaideen, K. et al. The role of wastewater treatment in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) and sustainability guideline. Energy Nexus. 7, 100112. 10.1016/j.nexus.2022.100112 (2022). - DOI
-
- Neris, J. B., Luzardo, F. H., Santos, P. F., de Almeida, O. N. & Velasco, F. G. Evaluation of single and tri-element adsorption of Pb2+, Ni2 + and Zn2 + ions in aqueous solution on modified water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) fibers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng.7, 102885 (2019). - DOI
-
- Sivakumar, D., Parthiban, R., Kumar, P. S. & Saravanan, A. Synthesis and characterization of ultrasonic-assisted Delonix regia seeds: modelling and application in dye adsorption. Desalin. Water Treat.173, 427–441 (2020). - DOI
-
- De Mattos, N. R., De Oliveira, C. R., Camargo, L. G. B., da Silva, R. S. R. & Lavall, R. L. Azo dye adsorption on anthracite: A view of thermodynamics, kinetics and cosmotropic effects. Sep. Purif. Technol.209, 806–814 (2019). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

