Hypertension among people living with HIV receiving dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy in ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40603478
- PMCID: PMC12223162
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06145-z
Hypertension among people living with HIV receiving dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy in ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
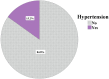
Recently, dolutegravir (DTG) has been associated with weight gain, dyslipidemia, and hyperglycemia, which in turn raise(s) the risk of hypertension. However, little is known about the burden of hypertension among people living with HIV (PLHIV) taking DTG-based therapy in Ethiopia. This study aimed to assess the prevalence and factors associated with hypertension among PLHIV taking DTG-based therapy. We conducted a cross-sectional study on 415 selected PLHIV aged 18 years or older who had been on DTG-based therapy for at least six months at the antiretroviral therapy (ART) clinic of Dessie Comprehensive Specialized Hospital from February 5 to April 5, 2023. Participants with a diagnosis of hypertension before DTG-based ART initiation, pregnant women, and patients who were seriously ill and unable to respond were excluded from the study. Data on sociodemographic, behavioral, and clinical characteristics were collected using a structured questionnaire and patient chart review. Blood pressure, anthropometric, and biochemical measurements were done. Hypertension was defined as systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg and 90 mmHg, respectively. A multivariable logistic regression was carried out to determine factors associated with hypertension. Variables with a p-value < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The prevalence of hypertension was 15.2% (95% CI: 11.9-19). Sex (AOR = 3.01, 95% CI: 1.56-5.79, p = 0.001), duration of taking DTG-based therapy (AOR = 3.61, 95% CI: 1.72-7.59, p = 0.001), family history of hypertension (AOR = 3.51, 95% CI: 1.54-8.04, p = 0.003), body mass index (BMI) (AOR = 1.92, 95% CI: 1.02-3.64, p = 0.044), and fasting blood glucose level (FBG) (AOR = 2.33, 95% CI: 1.01-5.39, p = 0.047) were significantly associated with hypertension among PLHIV on DTG-based ART in Ethiopia. Hypertension is not uncommon in PLHIV taking DTG-based therapy. Sex, duration of taking DTG-based therapy, family history of hypertension, BMI, and FBG levels were significant correlates of hypertension among PLHIV taking DTG-based therapy. These findings highlight the need for routine hypertension screening and lifestyle interventions for PLHIV on DTG-based therapy, particularly among males, those with prolonged use of DTG-based therapy, a family history of hypertension, elevated BMI, or increased FBG.
Keywords: ART; Dolutegravir (DTG); HIV; Hypertension; People living with HIV (PLHIV).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence and determinants of metabolic syndrome among adults living with HIV on first-line antiretroviral treatment in southern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2025 Jun 21;16:20406223251346289. doi: 10.1177/20406223251346289. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2025. PMID: 40546308 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with hyperglycemia among persons living with HIV/AIDS on dolutegravir-based antiretroviral therapy in Uganda.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 10;11:20499361241272630. doi: 10.1177/20499361241272630. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39286262 Free PMC article.
-
Drug induced liver injury in HIV patients on dolutegravir based antiretroviral therapy regimens in Wolaita Sodo comprehensive specialized hospital.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 31;15(1):28013. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13504-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40744986 Free PMC article.
-
Health related quality of life and its association with social support among people living with HIV/AIDS receiving antiretroviral therapy in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022 May 8;20(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-01985-z. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022. PMID: 35527300 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
References
-
- (WHO) WHO & Hypertension [ (2021). Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
-
- Albrecht, S. et al. Age-related comorbidities and mortality in people living with HIV in rural Tanzania. AIDS (London England). 33 (6), 1031–1041 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous