Multimodal AI to forecast arrhythmic death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 40603582
- PMCID: PMC12259465
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-025-00679-1
Multimodal AI to forecast arrhythmic death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
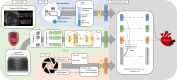
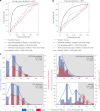
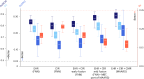
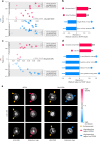
Sudden cardiac death from ventricular arrhythmias is a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Arrhythmic death prognostication is challenging in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a setting where current clinical guidelines show low performance and inconsistent accuracy. Here, we present a deep learning approach, MAARS (Multimodal Artificial intelligence for ventricular Arrhythmia Risk Stratification), to forecast lethal arrhythmia events in patients with HCM by analyzing multimodal medical data. MAARS' transformer-based neural networks learn from electronic health records, echocardiogram and radiology reports, and contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance images, the latter being a unique feature of this model. MAARS achieves an area under the curve of 0.89 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.79-0.94) and 0.81 (95% CI 0.69-0.93) in internal and external cohorts and outperforms current clinical guidelines by 0.27-0.35 (internal) and 0.22-0.30 (external). In contrast to clinical guidelines, it demonstrates fairness across demographic subgroups. We interpret MAARS' predictions on multiple levels to promote artificial intelligence transparency and derive risk factors warranting further investigation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


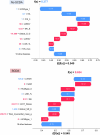
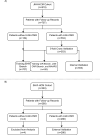
References
-
- John, R. M. et al. Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Lancet380, 1520–1529 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Rea, T. D. & Page, R. L. Community approaches to improve resuscitation after out-of-hospital sudden cardiac arrest. Circulation121, 1134–1140 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Estes, N. A. M. 3rd Predicting and preventing sudden cardiac death. Circulation124, 651–656 (2011). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL166759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL174440/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01HL166759/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01 HL174440/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35HL1431598/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
