Recent advances in cardiovascular disease research driven by metabolomics technologies in the context of systems biology
- PMID: 40603608
- PMCID: PMC12118667
- DOI: 10.1038/s44324-024-00028-z
Recent advances in cardiovascular disease research driven by metabolomics technologies in the context of systems biology
Abstract
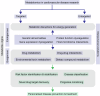
Traditional risk factors and biomarkers of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) have been mainly discovered through clinical observations. Nevertheless, there is still a gap in knowledge in more sophisticated CVD risk factor stratification and more reliable treatment outcome prediction, highlighting the need for a more comprehensive understanding of disease mechanisms at the molecular level. This need has been addressed by integrating information derived from multiomics studies, which provides systematic insights into the different layers of the central dogma in molecular biology. With the advancement of technologies such as NMR and UPLC-MS, metabolomics have become a powerhouse in pharmaceutical and clinical research for high-throughput, robust, quantitative characterisation of metabolic profiles in various types of biospecimens. In this review, we highlight the versatile value of metabolomics spanning from targeted and untargeted identification of novel biomarkers and biochemical pathways, to tracing drug pharmacokinetics and drug-drug interactions for more personalised medication in CVD research (Fig. 1).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gaziano, T., Reddy, K. S., Paccaud, F., Horton, S. & Chaturvedi, V. Cardiovascular Disease. in Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. 2nd edition (The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank, 2006). - PubMed
-
- Achievements in Public Health, 1900-1999: Decline in Deaths from Heart Disease and Stroke -- United States, 1900-1999. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm4830a1.htm.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
