SLC34A2 inhibits tumorigenesis and progression via upregulating LRRK2/TTF-1/SELENBP1 axis in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40603644
- PMCID: PMC12353814
- DOI: 10.1038/s41417-025-00928-2
SLC34A2 inhibits tumorigenesis and progression via upregulating LRRK2/TTF-1/SELENBP1 axis in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
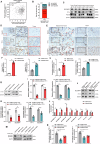
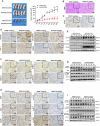
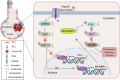
Alveolar type II epithelial (AT2) cells have the properties of stem cells, abnormal AT2 cells serve as one of the original cells in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). However, the abnormal genes expression of AT2 cells during their malignant transformation into LUAD cells remain poorly understood. Importantly, SLC34A2 is a specific gene in AT2 cells of the lung. Our previous researches have reported that overexpression of SLC34A2 significantly inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of LUAD cells. But, the underlying mechanisms of SLC34A2 in LUAD are largely unknown until now. Here, the present study discovered that the protein expression of Napi2b (SLC34A2), SELENBP1, TTF-1 and LRRK2 were all located in human AT2 cells of adjacent non-tumor tissues. However, the expression level of SLC34A2, SELENBP1, TTF-1 and LRRK2 were significantly decreased in LUAD tissues, and the expression of SLC34A2 was obviously positive correlation with the expression of SELENBP1, TTF-1 and LRRK2, respectively. Mechanistically, our study elucidated that overexpression of SLC34A2 could inhibit the activation of MEK/ERK signaling pathway through up-regulating the expression of LRRK2, and subsequently suppressed the expression of p-TTF-1(Ser327), which upregulated the expression of SELENBP1 by enhancing TTF-1 transcriptional activity. Ultimately, overexpression of SLC34A2 depressed the activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway via up-regulating the expression of SELENBP1, which significantly inhibited the malignant characteristics of LUAD. In summary, our current research revealed a novel SLC34A2/LRRK2/TTF-1/SELENBP1 axis and its involvement in inhibiting the malignant characteristics of LUAD cells for the first time, which made contribution to further exploring the clinical application of SLC34A2. Furthermore, it also might offer novel insights into understanding how AT2 cells undergo malignant transformation into LUAD cells in the future.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Figure 7 was drawn by Figdraw ( www.figdraw.com ). Ethics approval and consent to participate: All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. The clinical samples study was approved by the West China Hospital of Sichuan University Biomedical Research Ethics Committee and the Medical Ethics Committee, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences, Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital (NO.2023-138). This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from each patient. The animal experiments and all procedures involving the handling and treatment of mice during this study were approved by Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of West China Hospital (NO.20220721002), Sichuan University (Chengdu, China). All the experiments were performed according to the guidelines of the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via EGFR degradation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05259-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594106 Free PMC article.
-
SMC2 knockdown inhibits malignant progression of lung adenocarcinoma by upregulating BTG2 expression.Cell Signal. 2024 Aug;120:111216. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111216. Epub 2024 May 8. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38729325
-
Single-cell transcriptomic profiling reveals the heterogeneity of epithelial cells in lung adenocarcinoma lymph node metastasis and develops a prognostic signature.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 25;16:1637625. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1637625. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40787454 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in the genetic variant spectrum of SLC34A2 in pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis; a systematic review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023 May 31;18(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s13023-023-02712-7. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023. PMID: 37259144 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage rewiring in lung adenocarcinoma via HNF4α and NKX2-1 dynamics.Genes Dev. 2025 Sep 2;39(17-18):993-994. doi: 10.1101/gad.353142.125. Genes Dev. 2025. PMID: 40707360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Omics Reveal Dendrobium nobile Lindl.'s Anti-Diabetic Mechanisms via Arginine/Proline and Glycerophospholipid Pathways.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;18(7):1061. doi: 10.3390/ph18071061. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–63. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, Mariotto AB, Yabroff KR, Jemal A, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:409–36. - PubMed
-
- Guillot L, Nathan N, Tabary O, Thouvenin G, Le Rouzic P, Corvol H, et al. Alveolar epithelial cells: master regulators of lung homeostasis. Int J Biochem cell Biol. 2013;45:2568–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

