Glucosamine activates intestinal P-glycoprotein inhibiting drug absorption
- PMID: 40603843
- PMCID: PMC12222954
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61437-2
Glucosamine activates intestinal P-glycoprotein inhibiting drug absorption
Abstract
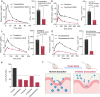
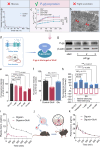
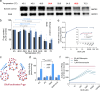
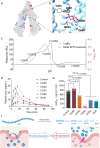
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is a crucial drug efflux transporter in the gastrointestinal tract, reducing drug uptake and expelling harmful xenobiotics to prevent pathological changes. Current P-gp enhancers primarily increase P-gp expression, requiring 1-3 days, thus missing the critical rescue window for acute poisoning. This study identifies glucosamine (GlcN) as a potent P-gp activator that swiftly enhances drug efflux, significantly reducing drug absorption without altering P-gp expression levels. GlcN directly binds to P-gp, boosting its transport efficiency. Only GlcN with a polymerization degree below 5 can activate P-gp, whereas higher polymerized chitooligosaccharides enhance drug absorption. Additionally, GlcN activation of P-gp has significant implications for cellular metabolism by expelling xenobiotics and metabolic by-products, maintaining cellular homeostasis. Our findings suggest GlcN's potential as an effective antidote for paraquat poisoning and offer a detoxification strategy. This research provides a foundational understanding for developing improved detoxification agents and metabolic modulators.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

