Loss of endothelial ZEB2 in mice attenuates steatosis early during metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
- PMID: 40603966
- PMCID: PMC12222841
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05881-6
Loss of endothelial ZEB2 in mice attenuates steatosis early during metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Abstract
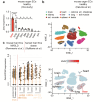
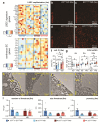
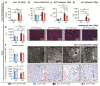
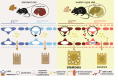
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, features liver sinusoidal endothelial cell (LSEC) alterations with ill-defined driving factors. Zinc-Finger E-Box-binding Homeobox (ZEB)2 in LSECs preserves their specialized features, prevents capillarization and protects against liver fibrosis. To investigate a potential protective role against steatosis, the initial MASLD stage, we fed EC-specific Zeb2 knockout (ECZeb2KO) mice a western-type diet (WD). In healthy and steatotic wild-type livers, Zeb2 was ubiquitously and similarly expressed across blood-vascular EC types. LSEC RNA sequencing revealed ZEB2 deficiency-triggered expression changes greatly overlapping with those evoked by WD-feeding. Endothelial ZEB2-loss and WD-feeding interacted to boost capillarization and fat metabolism, shown by increased expression of continuous EC markers and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)α signaling components, respectively. Altered communication among LSECs after combined endothelial ZEB2-loss and WD-exposure revealed similar functional repercussions. Endothelial ZEB2-loss eventually corrected WD-induced liver hypo-vascularization while ameliorating hepatic damage and steatosis. Thus, endothelial ZEB2-loss amplifies WD-induced LSEC fat metabolism and capillarization, while decreasing steatosis, in part through altered LSEC-LSEC communication. The disease-promoting role of endothelial ZEB2 in early MASLD as opposed to its protective role in fibrosis underscores a context-dependent effect in liver disease.
Keywords: Capillarization; Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated receptor alpha; Zinc-finger E-Box-binding Homeobox 2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Aird, W. C. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ. Res.100, 174–190. 10.1161/01.RES.0000255690.03436.ae (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hammoutene, A. & Rautou, P. E. Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol.70, 1278–1291. 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.012 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Shahani, T. et al. Human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells but not hepatocytes contain factor VIII. J. Thromb. Haemost. 12, 36–42. 10.1111/jth.12412 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Sorensen, K. K. et al. The scavenger endothelial cell: a new player in homeostasis and immunity. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.303, R1217–1230. 10.1152/ajpregu.00686.2011 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C12/16/023/KU Leuven (Katholieke Universiteit Leuven)
- C14/19/095/KU Leuven (Katholieke Universiteit Leuven)
- PF/10/014/KU Leuven (Katholieke Universiteit Leuven)
- FP7-StG-IMAGINED203291/EC | EC Seventh Framework Programm | FP7 Ideas: European Research Council (FP7-IDEAS-ERC - Specific Programme: "Ideas" Implementing the Seventh Framework Programme of the European Community for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities (2007 to 2013))
- WOG001420N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Research Foundation Flanders)
- 1157318N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Research Foundation Flanders)
- 1243121N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Research Foundation Flanders)
- 1S25817N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Research Foundation Flanders)
- WOG001420N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Research Foundation Flanders)
- G.0A3116/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (Research Foundation Flanders)
- IUAP/P7/07/Interuniversity Attraction Poles Grant
- FP7-Health-HemiBio266777/Cosmetics Europe/European Commission FP7 Grant
- H2020-MSCA-IF-REZONABLE658666/EC | EC Seventh Framework Programm | FP7 People: Marie-Curie Actions (FP7-PEOPLE - Specific Programme "People" Implementing the Seventh Framework Programme of the European Community for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities (2007 to 2013))
- H2020 848109-CRUCIAL/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Excellent Science (H2020 Priority Excellent Science)
- IUAP/P7/07/Interuniversity Attraction Poles Grant
- departmental funds/Erasmus University Rotterdam | Erasmus Universitair Medisch Centrum Rotterdam (Erasmus Universitair Medisch Centrum)
- BIG project funding/Erasmus University Rotterdam | Erasmus Universitair Medisch Centrum Rotterdam (Erasmus Universitair Medisch Centrum)
- 2018/23115|ZONMW/ZonMw (Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

