Influence of fermented whey protein fractions on the growth performance, haematological traits, serum biochemistry, faecal and caeca microbiota of broiler chickens
- PMID: 40604089
- PMCID: PMC12223115
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-09289-0
Influence of fermented whey protein fractions on the growth performance, haematological traits, serum biochemistry, faecal and caeca microbiota of broiler chickens
Erratum in
-
Correction: Influence of fermented whey protein fractions on the growth performance, haematological traits, serum biochemistry, faecal and caeca microbiota of broiler chickens.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27726. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13549-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40731069 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
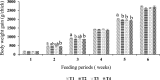
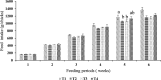
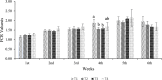
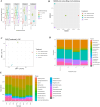
Nowadays researchers and consumers are concerned about antibiotic resistance in poultry products causing antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Here, we investigated the effects of fermented whey peptides (FWP) with Limosilactobacillus fermentum (M4) as a nutraceutical supplement on growth performance, blood parameters, relative organs, and metagenomic analysis of broiler chickens, aiming to develop substitute for antibiotics in poultry feeds. An active culture of Lactobacillus fermentum (M4, GenBank Accession Number: MF951096) was inoculated into sterilized cheese whey at a rate of 2% (v/v) (107 CFU/ml) and incubated at 37 °C for 48 h. Ninety-six one-day-old mixed-sex commercial broiler chicks were randomly assigned in a Completely Randomized Design (CRD) experiment with four treatments, each having four replicates of six broiler chickens (6 × 4 × 4). One millilitre of liquid FWP fractions (> 10 kDa, < 10 kDa, and < 3 kDa) was freshly prepared and administered daily to the respective groups along with the basal diet from the 8th to the 15th day. Our current study revealed that supplementation with FWPs to broiler diets had no significant (p < 0.05) impact on body weight and FCR but numerically FCR value was high in control group. Blood cholesterol was significantly reduced in FWP fed groups. FWP had no significant impact on various blood parameters but influenced leukocytes and platelets. Metagenomic analysis showed no significant differences in microbial proportions. Histological analysis revealed no organ toxicity. The current findings suggest that broiler diets can substitute FWP for antibiotics to improve the growth performance and birds' health, without posing any biohazards. Furthermore, FWPs provide a variety of health benefits, potentially improving the health of humans who consume broiler meat or eggs.
Keywords: Blood cholesterol; Broiler birds; Cheddar cheese whey; Lactobacillus; Metagenome; Whey peptides.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: All authors have read and approved the revised manuscript and informed of the submission to Scientific Reports. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures



References
-
- Buchanan, D., Martindale, W., Romeih, E. & Hebishy, E. Recent advances in whey processing and valorisation: technological and environmental perspectives. Int. J. Dairy Technol.76(2), 291–312. 10.1111/1471-0307.12935 (2023).
-
- Bintsis, T. & Papademas, P. Sustainable approaches in whey cheese production: a review. Dairy4(2), 249–270. 10.3390/dairy4020018 (2023).
-
- Pal, S., McKay, J., Jane, M. & Ho, S. Dairy whey proteins and obesity. In Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Abdominal Obesity 261–278 (Academic Press, 2019). 10.1016/B978-0-12-816093-0.00020-3.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

