KMnO4/Pb staining allows uranium free imaging of tissue architectures in low vacuum scanning electron microscopy
- PMID: 40604145
- PMCID: PMC12118665
- DOI: 10.1038/s44303-024-00045-z
KMnO4/Pb staining allows uranium free imaging of tissue architectures in low vacuum scanning electron microscopy
Abstract
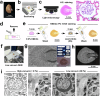
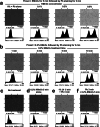
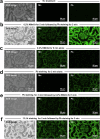
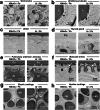
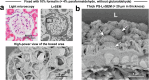
Scanning electron microscopy under low-vacuum conditions allows high-resolution imaging of complex cell/tissue architectures in nonconductive specimens. However, the conventional methods for metal staining of biological specimens require harmful uranium compounds, which hampers the applications of electron microscopy. Here, we introduce a uranium-free KMnO4/Pb metal staining protocol that allows multiscale imaging of extensive cell/tissue architectures to intensive subcellular ultrastructures. The obtained image contrast was equivalent to that of Ur/Pb staining and sufficient for ultrastructural observation, showing the fine processes of podocytes in the glomerulus, which were invisible by light microscopy. The stainability in the elastic tissue indicated that the distinct histochemical properties of KMnO4 oxidation led to Pb deposition and BSE signal enhancement superior to Ur staining. Elemental analysis clarified that the determinant of the backscattered electron signal intensity was the amount of Pb deposition enhanced by KMnO4 oxidation. This user-friendly method is anticipated to create a new approach for biomedical electron microscopy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
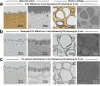
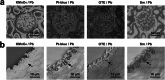
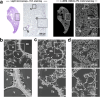
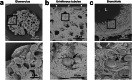
References
-
- Griffiths, G. Ultrastructure in cell biology: do we still need it? Eur. J. Cell Biol.83, 245–251 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Knott, G. & Genoud, C. Is EM dead? J. Cell Sci.126, 4545–4552 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Ochs, M. et al. Using electron microscopes to look into the lung. Histochem. Cell Biol.146, 695–707 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Danilatos, G. Mechanisms of detection and imaging in the ESEM. J. Microsc.160, 9–19 (1989).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
