Large language model trained on clinical oncology data predicts cancer progression
- PMID: 40604229
- PMCID: PMC12223279
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01780-2
Large language model trained on clinical oncology data predicts cancer progression
Abstract
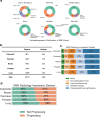
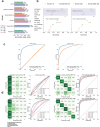
Subspecialty knowledge barriers have limited the adoption of large language models (LLMs) in oncology. We introduce Woollie, an open-source, oncology-specific LLM trained on real-world data from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) across lung, breast, prostate, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers, with external validation using University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) data. Woollie surpasses ChatGPT in medical benchmarks and excels in eight non-medical benchmarks. Analyzing 39,319 radiology impression notes from 4002 patients, it achieved an overall area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.97 for cancer progression prediction on MSK data, including a notable 0.98 AUROC for pancreatic cancer. On UCSF data, it achieved an overall AUROC of 0.88, excelling in lung cancer detection with an AUROC of 0.95. As the first oncology specific LLM validated across institutions, Woollie demonstrates high accuracy and consistency across cancer types, underscoring its potential to enhance cancer progression analysis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ouyang, L. et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst.35, 27730–27744 (2022).
-
- OpenAi. GPT-4 technical report (OpenAi, 2023).
-
- Eloundou, T., Manning, S., Mishkin, P. & Rock, D. Gpts are gpts: an early look at the labor market impact potential of large language models. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.10130 (2023).
-
- Will ChatGPT transform healthcare? Nat. Med.29, 505–506 (2023) - PubMed
-
- Nori, H., King, N., McKinney, S. M., Carignan, D. & Horvitz, E. Capabilities of gpt-4 on medical challenge problems. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.13375 (2023).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

