Jasmonic acid-mediated cell wall biosynthesis pathway involved in pepper (Capsicum annuum) defense response to Ralstonia solanacearum
- PMID: 40604413
- PMCID: PMC12218943
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06784-4
Jasmonic acid-mediated cell wall biosynthesis pathway involved in pepper (Capsicum annuum) defense response to Ralstonia solanacearum
Abstract
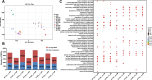
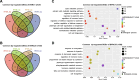
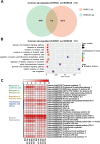
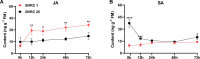
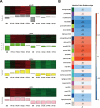
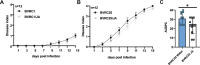
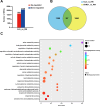
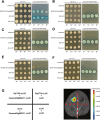
Ralstonia solanacearum is a destructive soil-borne pathogen that causes severe bacterial wilt (BW) disease in peppers. Phytohormone signaling pathways, including those mediated by jasmonic acid (JA), are crucial to plant defense responses against pathogen attacks. Nevertheless, the function of JA in the resistance response of pepper to R. solanacearum is unclear. Therefore, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and phytohormone determination experiments were performed to compare the dynamic transcriptome changes and differences in JA and salicylic acid (SA) contents between the resistant pepper line BVRC1 and the susceptible pepper line BVRC25 during R. solanacearum infection. The number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was greater in BVRC1 than in BVRC25 at 12, 24, 48, and 72 h post-infection. JA concentrations were also markedly elevated in BVRC1 in response to R. solanacearum. Four distinct co-expression modules and hub genes were identified using weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Exogenous application of JA significantly delayed the onset of R. solanacearum infection and reduced symptom severity in BVRC25. RNA-seq was performed on the resistant pepper line BVRC1 at 24 h post exogenous JA application. GO analysis revealed DEGs enriched in the cell wall biosynthesis-related pathway of BVRC1 after JA treatment. Notably, a pathogenesis-related protein, Capana08g002211, exhibited common up-regulated patterns in response to JA treatment and R. solanacearum infection. A yeast-2-hybrid assay and luciferase complementation imaging assay demonstrated that Capana08g002211 interacted with type III effector (RipTPS). These results demonstrate that the pepper JA-mediated cell wall synthesis pathway participates in the defense response to R. solanacearum.
Keywords: Capsicum annuum; Ralstonia solanacearum; Bacterial wilt; Jasmonic acid (JA); Transcriptome; Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pleiotropic Phenotypes of the Tomato diageotropica Mutant Enable Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2025 Jul;38(4):566-578. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-24-0123-R. Epub 2025 Aug 11. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2025. PMID: 40281390
-
Ralstonia solanacearum Type III Effector RipAL Targets Chloroplasts and Induces Jasmonic Acid Production to Suppress Salicylic Acid-Mediated Defense Responses in Plants.Plant Cell Physiol. 2018 Dec 1;59(12):2576-2589. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcy177. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30165674
-
CaASR1 promotes salicylic acid- but represses jasmonic acid-dependent signaling to enhance the resistance of Capsicum annuum to bacterial wilt by modulating CabZIP63.J Exp Bot. 2020 Oct 22;71(20):6538-6554. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa350. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32720981
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
Key mechanisms of plant-Ralstonia solanacearum interaction in bacterial wilt pathogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1521422. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1521422. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40547798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lowe-Power TM, Khokhani D, Allen C. How Ralstonia solanacearum exploits and thrives in the flowing plant xylem environment. Trends Microbiol. 2018;26:929–42. - PubMed
-
- Rivera-Zuluaga K, Hiles R, Barua P, Caldwell D, Iyer-Pascuzzi AS. Getting to the root of Ralstonia invasion. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2023;148–149:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Du H, Chen B, Zhang X, Zhang F, Miller SA, Rajashekara G, et al. Evaluation of Ralstonia solanacearum infection dynamics in resistant and susceptible pepper lines using bioluminescence imaging. Plant Dis. 2017;101:272–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BAIC01-2024-02/Beijing Innovation consortium of Agriculture Research System
- 32072565/National Science Foundation of China
- KJCX20210421/Construction Program of Science and Technology Innovation Capability of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences
- XTCX202303/Beijing Vegetable Research center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

