Retrospective cohort of prenatal home ultrasound utilization and maternal-neonatal outcomes
- PMID: 40604476
- PMCID: PMC12219377
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-025-07664-3
Retrospective cohort of prenatal home ultrasound utilization and maternal-neonatal outcomes
Abstract
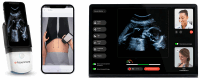
Background: Telehealth solutions, including ultrasound technology, are sought as a modality to enhance prenatal. We aimed to evaluate the utilization of a self-operated home ultrasound service in a real-world large cohort, comparing users vs. non-users. This service provides a handheld, app-connected ultrasound device for remote basic fetal monitoring, with its use determined at the discretion of the patient as a supplement - rather than a replacement - to standard prenatal care.
Methods: Retrospective analysis comparing maternal and neonatal outcomes among users versus non-users of the home ultrasound service, between January 2020 and December 2022. Primary outcome measures were preterm delivery and a composite adverse neonatal outcome. Confounders were balanced between the groups using nearest neighbour matching with propensity scores. Multivariable analyses including the confounders were conducted in matched cohorts to obtain doubly robust estimates. A sensitivity analysis included those who began using the device before 22 gestational weeks and continued for more than 10 weeks. Safety was assessed by identifying any maternal, obstetrical, or neonatal complications plausibly linked to device use.
Results: The study compared two cohorts; the exposed cohort of 4,460 pregnant women using Clalit's home ultrasound service (users), and the control (non-users) cohort of 102,707 pregnant women with an equal HMO insurance status. Users had higher socioeconomic scores, were more primiparous and had a higher incidence of chronic disease and pregnancy complications. Preterm birth rates and adverse neonatal outcomes did not differ between groups. Device utilization, both overall and stratified by actual utilization degree, was safe and not associated with any maternal, obstetrical or neonatal adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Conclusions: A self-operated home ultrasound device, during the second and third trimester, is safe and not significantly associated with any pregnancy adverse event or neonatal complications.
Keywords: Home; Mobile; Outcome; Pregnancy; Remote; Safety; Telehealth; Ultrasound.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The research related to human use has been compiled with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki declaration. The study received approval from the local institutional review board at Rabin Medical Center, Petach-Tikva; Israel (Approval Number: 744-RMC-21). Informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study. Consent for publication: Written informed consent for publication was obtained. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hadar E, Wolff L, Tenenbaum-Gavish K, Eisner M, Shmueli A, Barbash-Hazan S, Bergel R, Shmuel E, Houri O, Dollinger S, Brzezinski-Sinai NA, Sukenik S, Pardo A, Navon I, Wilk Y, Zafrir-Danieli H, Wiznitzer A. Mobile Self-Operated home ultrasound system for remote fetal assessment during pregnancy. Telemed J E Health. 2022;28(1):93–101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Axelrod M, Lahav Ezra M, Galler E, et al. Putting the fetus back in maternal-fetal telemedicine: a prospective pilot study. AJOG. 2024;228(1 Suppl):S544.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

