A surveillance-based epidemiological study of renal agenesis in 25 million births in china, 2007-2020
- PMID: 40604648
- PMCID: PMC12225177
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-025-07807-6
A surveillance-based epidemiological study of renal agenesis in 25 million births in china, 2007-2020
Abstract
Background: Renal agenesis (RA), a rare congenital kidney defect, varies in clinical severity. Unilateral renal agenesis (URA) is more prevalent and may cause long-term renal complications, whereas bilateral renal agenesis (BRA) is typically fatal. While epidemiological data on RA is limited in China, understanding its prevalence and associated factors is crucial for public health interventions.
Methods: We conducted a prevalence analysis using data from the Chinese Birth Defects Monitoring Network between 2007 and 2020. Prevalence rates of RA, URA, and BRA were calculated and stratified by birth year, maternal age, residence area, geographical region, and infant sex. Temporal trends in prevalence were examined. We also investigated pregnancy outcomes among affected infants, including preterm births, low birth weight, early neonatal deaths, and termination of pregnancy for fetal anomaly (TOPFA). Furthermore, co-occurring congenital anomalies were assessed. Poisson regression analysis was used to assess the distribution of URA and BRA across residential areas and geographic regions and to identify factors associated with their prevalence.
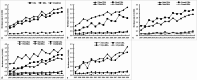
Results: Among 25,909,000 births between 2007 and 2020, a total of 5,906 cases of RA were identified (5,020 URA and 780 BRA). The prevalence rates per 10,000 live and still births were 2.28 for RA, 1.94 for URA, and 0.30 for BRA, all showing an increasing trend over the study period. Compared to URA, BRA was significantly associated with a higher proportion of preterm birth, low birth weight, early neonatal death, and TOPFA. Poisson regression analysis revealed a consistent distribution of URA and BRA across residential areas and geographic regions, with higher prevalence observed in urban areas and the eastern and central regions of China. Maternal age < 35 years and female sex were associated with a higher prevalence of URA, while male sex was associated with a higher prevalence of BRA. Both URA and BRA frequently co-occurred with congenital malformations of the circulatory, urinary, and musculoskeletal systems.
Conclusions: The study provides the first comprehensive epidemiological assessment of RA in China. The increasing prevalence and distinct differences in the pregnancy outcomes between URA and BRA underscore the importance of timely prenatal diagnosis and appropriate counseling for affected families.
Keywords: Chinese; Epidemiology; Prevalence rate; Renal agenesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participants: The Medical Ethics Committee of the West China Second University Hospital, Sichuan University reviewed and approved this study, granting a waiver of informed consent for this retrospective analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unilateral renal agenesis: a systematic review on associated anomalies and renal injury.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Jul;28(7):1844-55. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft012. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23449343
-
Gestational weight gain below instead of within the guidelines per class of maternal obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of obstetrical and neonatal outcomes.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022 Sep;4(5):100682. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2022.100682. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2022. PMID: 35728780
-
Different corticosteroids and regimens for accelerating fetal lung maturation for babies at risk of preterm birth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 9;8(8):CD006764. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006764.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35943347 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple-micronutrient supplementation for women during pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 13;4(4):CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 14;3:CD004905. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004905.pub6. PMID: 28407219 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Analysis on the prevalence and temporal trends of adverse birth outcomes among neonates in Shanghai from 2010 to 2023.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 18;13:1563613. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1563613. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40756393 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 2017YFC0907304/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2017YFC0907304/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2017YFC0907304/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2017YFC0907304/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2017YFC0907304/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

