Cerebrospinal fluid sTREM2 mediates the associations of α-synuclein with tau pathology in older adults without dementia: two population-based study
- PMID: 40604812
- PMCID: PMC12225095
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06729-3
Cerebrospinal fluid sTREM2 mediates the associations of α-synuclein with tau pathology in older adults without dementia: two population-based study
Abstract
Background: The role of microglial activation by α-synuclein in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the role of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (sTREM2) in regulating the relationship between α-synuclein and tau pathology in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Methods: A total of 989 participants were included in the CABLE (Chinese Alzheimer’s Biomarker and LifestylE) study. Multiple linear regression analyses were performed to assess the associations of CSF α-synuclein and sTREM2 with tau pathology. Causal mediation analyses with 10,000 bootstrap iterations were conducted to investigate the mediating effect of sTREM2 on the relationship between α-synuclein and tau pathology. Additionally, subgroup analyses were performed based on APOE ε4 carrier status. The same analytical method was applied to the ADNI (Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative) cohort for validation. Furthermore, Cox proportional hazards models were employed to evaluate the longitudinal association between α-synuclein levels and the risk of AD in the ADNI cohort. Causal mediation analysis further evaluated the mediating role of tau pathology in the relationship between α-synuclein and the risk of AD.
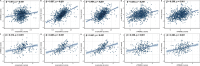
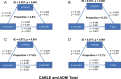
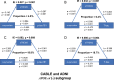
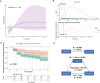
Results: In CABLE, elevated levels of α-synuclein were significantly associated with increased levels of sTREM2 (p < 0.001), p-tau181 (p < 0.001), and T-tau (p < 0.001). The relationship between α-synuclein and tau pathology was partially mediated by sTREM2, with mediation rates of 4.8% and 6.3%, respectively. Further subgroup analysis revealed that this mediating relationship was present only in APOE ε4 non-carriers. The CABLE findings were validated in the ADNI, with the proportion of mediators ranging from 17.1 to 18.8%. Additionally, higher levels of α-synuclein were linked to an increased risk of AD (hazard ratio = 2. 137, p = 0.006). The relationship between α-synuclein levels and the risk of AD was mediated by p-tau181 but not T-tau, with a mediation rate of 67.6%.
Conclusions: Overall, activated microglia partially mediate the α-synuclein-tau pathology association, while p-tau181 further mediates the relationship between α-synuclein and AD risk. Thus, targeting the CSF α-synuclein-microglia-tau pathological pathway provides new insights into the prevention and treatment of AD.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12967-025-06729-3.
Keywords: APOE ε4; Alzheimer’s disease; Cerebrospinal fluid; Microglia; Tau pathology; sTREM2; Α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The CABLE study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Qingdao Municipal Hospital. The ADNI study was approved by the institutional review boards of all participating centers ( https://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/how_to_apply/ADNI_Acknowledgement_List.pdf ). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

