Information quality of videos related to esophageal cancer on tiktok, kwai, and bilibili: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40604838
- PMCID: PMC12220660
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-23475-9
Information quality of videos related to esophageal cancer on tiktok, kwai, and bilibili: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Esophageal cancer typically lacks specific early symptoms, leading to late-stage diagnosis and poor prognosis, with an overall low 5-year survival rate. However, early detection and timely intervention can significantly improve the 5-year survival rate, underscoring the importance of prevention, screening, and early intervention. Short video platforms are increasingly utilized for health communication, offering opportunities to disseminate medical knowledge. However, the quality and reliability of health-related content, particularly for diseases like esophageal cancer, remain under explored.
Objective: This study aimed to systematically evaluate the quality, reliability, completeness, and engagement of esophageal cancer-related videos on three popular short video platform: Bilibili, TikTok, and Kwai, to identify platform-specific strengths and limitations in disseminating health information.
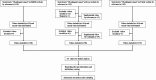
Methods: A total of 311 esophageal cancer-related videos were analyzed. Video assessment was assessed using 4 standardized scoring framework including General Quality Scores (GQS) for general quality, the DISCERN for reliability, Completeness Score (CS) for comprehensive information, Engagement Score (ES) for understandability and entertainment value of the video. Video features (source, category, content), user's behavior (likes, shares, comments) were also collected. Cross-platform comparisons were conducted to identify disparities in content quality and user interaction.
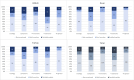
Results: This study analyzed 311 esophageal cancer-related videos on Bilibili, TikTok, and Kwai. Video quality varied significantly across platforms, with Bilibili showing the highest DISCERN (5.46), GQS (2.97) and CS (3.64), while TikTok videos achieved the highest ES (2.88) and engagement metrics (e.g., likes and collections, p < 0.001). Kwai videos had the lowest scores across all measures. Content focused primarily on "symptoms" and "treatment," with Bilibili offering more comprehensive coverage. Correlation analysis revealed a positive association between video quality and engagement on Bilibili but a negative association on TikTok (e.g., GQS and likes, r=-0.251, P = 0.009).
Conclusions: The quality of esophageal cancer-related videos across Bilibili, TikTok, and Kwai is suboptimal, with notable quality disparities among the platforms. Users on platforms other than Bilibili show limited ability to identify or prefer higher-quality content. This study underscores the potential of short-video platforms for esophageal cancer public health education, but highlights the need for improvements in content quality, ethical standards, and platform governance to address health equity concerns.
Keywords: Bilibili; DISCERN; Esophageal cancer; GQS; Information quality; Short video; Social media; TikTok.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quality and Dissemination of Uterine Fibroid Health Information on TikTok and Bilibili: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Aug 1;9:e75120. doi: 10.2196/75120. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40749219 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Video Content Quality of TikTok and Bilibili as Health Information Sources for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Rheum Dis. 2025 Jun;28(6):e70341. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70341. Int J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 40551617
-
Quality and Reliability of Adolescent Sexuality Education on Chinese Video Platforms: Sentiment-Topic Analysis and Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Form Res. 2025 Sep 5;9:e77100. doi: 10.2196/77100. JMIR Form Res. 2025. PMID: 40910701
-
Evaluating the quality of osteonecrosis and avascular necrosis content on youtube: a multidimensional analysis using DISCERN, JAMA, and GQS tools.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jul 22;20(1):695. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-06116-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40696472 Free PMC article.
-
YouTube as an information source for femoroacetabular impingement: a systematic review of video content.Arthroscopy. 2015 Jan;31(1):136-42. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Arthroscopy. 2015. PMID: 25150406
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung HYA. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-a Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Zeng HM, Chen WQ, Zheng RS, et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: a pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Global Health. 2018;6(5):e555–67. - PubMed
-
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(23):2241–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical