A scoping review of outcome selection and accuracy of conclusions in complex digital health interventions for young people (2017-2023): methodological proposals for population health intervention research
- PMID: 40604855
- PMCID: PMC12224660
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-025-04245-1
A scoping review of outcome selection and accuracy of conclusions in complex digital health interventions for young people (2017-2023): methodological proposals for population health intervention research
Abstract
Background: Determining the success of population health interventions often involves assessing multiple, multidimensional outcomes rather than a single one, which presents significant methodological challenges under the evidence-based medicine paradigm. This scoping review examines outcome selection, analysis, and interpretation, and the accuracy of conclusions in complex digital health interventions promoting health among adolescents and young adults (DHI-AYA).
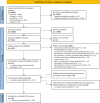
Methods: A comprehensive search of PubMed, EMBASE, ClinicalTrials.gov, PsycINFO, and CINAHL identified DHI-AYA implemented between 2017 and 2023. Studies were categorised by methodological choice regarding outcome hierarchical position: unique primary, multiple primary, or non-hierarchised outcomes. Outcomes were further classified into effectiveness, process, or economic categories. The authors' conclusions on intervention success were compared with conclusions drawn by the research team based on the reported outcome analysis strategy. Secondly, four analytical strategies were applied to a subset of selected interventions to illustrate the impact of outcome hierarchical position and number on conclusions about intervention success.
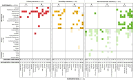
Results: Analysis of 100 studies linked to 26 DHI-AYA identified 251 distinct outcomes: 164 effectiveness, 78 process, and 9 economic outcomes. Seven interventions were evaluated using a unique primary outcome, 10 using multiple primary outcomes, and 9 using multiple non-hierarchised outcomes. Primary and secondary outcomes were predominantly effectiveness endpoints. The research team reclassified nine interventions (35%) deemed successful by authors as non-conclusive due to statistically conflicting results across outcomes. Most interventions deemed non-conclusive by the research team were evaluated using non-hierarchised outcomes (7/10, 70%). The choice of outcome analysis strategy substantially affected conclusions on intervention success.
Conclusions: Discrepancies in intervention success assessments highlight the need for enhanced transparency, robustness, and trustworthiness in conclusion-drawing processes. In response, five methodological proposals are formulated: (1) developing core outcome sets specific to population health intervention research (PHIR), (2) collaboratively selecting multidimensional outcomes through a steering committee that accounts for stakeholder preferences and existing theoretical models, (3) exploring multi-criteria decision analysis and consensus-driven methods to transparently combine outcomes, (4) enhancing methodological reporting through intervention development and evaluation to improve scientific integrity and reproducibility, and (5) increasing PHIR expert involvement in ethics, funding, and evaluation committees to improve recognition of evidence produced in this field.
Prospero registration number: CRD42023401979.
Keywords: Interventions; Methodological research; Outcomes; Population health intervention research; Scoping review.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Participation in environmental enhancement and conservation activities for health and well-being in adults: a review of quantitative and qualitative evidence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 21;2016(5):CD010351. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010351.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27207731 Free PMC article.
-
Quality improvement strategies for diabetes care: Effects on outcomes for adults living with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 31;5(5):CD014513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014513. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37254718 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for patients and caregivers to improve knowledge of sickle cell disease and recognition of its related complications.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 6;10(10):CD011175. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011175.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27711980 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of consumers and health providers working in partnership on health services planning, delivery and evaluation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 15;9(9):CD013373. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013373.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34523117 Free PMC article.
-
Housing improvements for health and associated socio-economic outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Feb 28;(2):CD008657. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008657.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23450585
References
-
- Fletcher RH, Fletcher SW, Wagner EH. Clinical epidemiology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1996.
-
- Sackett DL. Evidence-based medicine. Semin Perinatol. 1997;21(1):3–5. - PubMed
-
- Hawe P. Lessons from complex interventions to improve health. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015;36:307–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

