SHMT2 overexpression improves glaucoma by enhancing mitophagy in retinal ganglion cells through promoting the phospho of PINK1
- PMID: 40604870
- PMCID: PMC12220441
- DOI: 10.1186/s13000-025-01675-6
SHMT2 overexpression improves glaucoma by enhancing mitophagy in retinal ganglion cells through promoting the phospho of PINK1
Abstract
Background: Glaucoma is a major eye disease that causes blindness. The loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) due to mitophagy impairment is a key driver of glaucoma. SHMT2 depletion leads to an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS), but its role in regulating mitophagy remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the mechanism by which SHMT2 contributes to glaucoma through the regulation of RGC mitophagy.
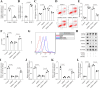
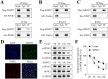
Methods: The role of SHMT2 in glaucoma was evaluated through hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining and immunofluorescence (IF) staining of acute ocular hypertension (AOH) mouse eyeballs. Mitophagy was assessed by measuring LDH release, apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential, lipid ROS, and the protein levels of mitophagy-related proteins in RGCs. The underlying mechanism was investigated using co-immunoprecipitation, IF staining, and Western blot analysis.
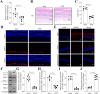
Results: Results showed that SHMT2 expression was decreased in the AOH mouse model. NMDA inhibited mitophagy in RGCs, which was restored by SHMT2 overexpression. Moreover, SHMT2 overexpression stabilized PINK1 expression by enhancing the phosphorylation of PINK1. In vivo experiments suggested that SHMT2 overexpression increased the thickness of the retinal ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer.
Conclusion: This study confirmed that SHMT2 overexpression alleviated glaucoma by enhancing mitophagy in RGCs through the upregulation of PINK1 phosphorylation, suggesting that SHMT2 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for glaucoma.
Keywords: Glaucoma; Mitophagy; PINK1; Retinal ganglion cells; SHMT2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Xinshijie Dongqu Eye Hospital. This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. All animal experiments should comply with the ARRIVE guidelines. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

