ARTEMISIA: a mechanistic study of a novel Janus kinase 1 inhibitor to advance molecular understanding and precision medicine in asthma
- PMID: 40604958
- PMCID: PMC12225079
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-025-03309-3
ARTEMISIA: a mechanistic study of a novel Janus kinase 1 inhibitor to advance molecular understanding and precision medicine in asthma
Abstract
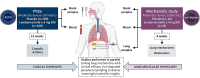
Background: Patients with uncontrolled asthma despite the use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS), may have a variety of biological pathways driving their airway inflammation. Londamocitinib (AZD4604), a selective, inhaled, Janus kinase 1 inhibitor, has been designed to target a broad inflammatory cytokine profile including those classically unresponsive to ICS. The ARTEMISIA mechanistic study aims to provide a clear understanding of the pathways impacted by londamocitinib in the lung, determine how this impact is reflected in the nose and periphery, and identify candidate biomarkers of londamocitinib-treatment response in asthma. This article reports the design and objectives of the ARTEMISIA study.
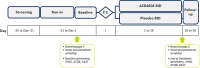
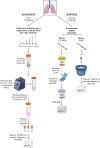
Methods: ARTEMISIA is a placebo-controlled, double-blind study of adults with moderate-to-severe asthma aiming to assess the effects of inhaled londamocitinib on Type 2 (T2) and non-T2 driven inflammatory pathways. Extensive parallel bio-sampling of the lung target tissue, nasal mucosa, blood and urine will be performed prior to the first dose and after 4-weeks of treatment with either londamocitinib or placebo. The main objectives of the study are to evaluate the effect of londamocitinib on gene expression in endobronchial brushings and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) phosphorylation in endobronchial biopsies. Key exploratory objectives include investigating the correlation between inflammatory phenotype-specific bronchial epithelial gene signatures and other biomarkers in the lung and peripheral samples; as well as analysis of transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic biomarkers in the nose, blood, and urine.
Discussion: ARTEMISIA commenced recruitment in 2024 and is poised to deliver a deep understanding of the mechanism of action of londamocitinib and its potential to impact on a population of asthmatics with high unmet need. The multiomic analysis of paired central and peripheral samples may reveal novel insights into the connection and translation between these compartments, deepen understanding of airways disease, and identify novel candidate biomarkers for asthma and JAK activity. In addition to sampling the airway directly, with parallel nasal and peripheral bio-sampling mirrored by the Phase 2a AJAX study (NCT06020014), the ARTEMISIA study may provide a unique link between bronchial assessed mechanisms of action and clinical outcomes.
Trial registration: NCT06435273 (ClinicalTrials.gov). Registered 24th May 2024.
Keywords: Asthma; Bronchoscopy; Gene signatures; Inflammation; Interferon-gamma; Interleukin-6; Janus kinase 1; Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT); T2; TH17.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Written informed consent was and will be obtained from all participants before enrolment into the study. The study is being conducted in accordance with the principles established in the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Council for Harmonisation Good Clinical Practice Guideline. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: CEB has received grants and consultancy fees from 4D Pharma, Areteia, AstraZeneca, Chiesi, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Mologic, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Roche and Sanofi. DPSD has received grants and consultancy fees from GlaxoSmithKline, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim and Synairgen. DPSD, ED, TJJ, ZJ, AH, MC, RH, AP and SG are employees of AstraZeneca and may own stock and/or stock options in AstraZeneca.
Figures


References
-
- Global Initiative For Asthma. Global Stratgey for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2024.
-
- Rabe KF, Nair P, Brusselle G, Maspero JF, Castro M, Sher L, Zhu H, Hamilton JD, Swanson BN, Khan A, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in Glucocorticoid-Dependent severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2475–85. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson M, Berggren K, Berglund S, Cerboni S, Collins M, Dahl G, Elmqvist D, Grimster NP, Hendrickx R, Johansson JR, et al. Discovery of the potent and selective inhaled Janus kinase 1 inhibitor AZD4604 and its preclinical characterization. J Med Chem. 2023;66:13400–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

