Combination of astragalus polysaccharide with Diosbulbin B exerts an enhanced antitumor effect in BRAFmut papillary thyroid cancer with decreased liver toxicity
- PMID: 40604967
- PMCID: PMC12224579
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03853-4
Combination of astragalus polysaccharide with Diosbulbin B exerts an enhanced antitumor effect in BRAFmut papillary thyroid cancer with decreased liver toxicity
Abstract
Background: Diosbulbin B (DB) is a traditional Chinese medicine used for thyroid cancer treatment, but always brings severe liver injury. In the current study, we investigated the role of astragalus polysaccharide (APS) in DB-induced hepatotoxicity and their anti-tumor effect on BRAFmut papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), and disclosed the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Two BRAFmut PTC IHH-4 and GLAG-66 cell lines were applied for the in vitro assays. CCK-8, flow cytometry, transwell chambers, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were performed for cell growth, apoptosis, migration/invasion, malondialdehyde (MDA)/glutathione (GSH) content and mitochondria damage detection. Human normal liver epithelial cell line THLE-2 was used to assess the liver toxicity, together with the animal experiment.
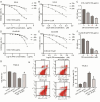
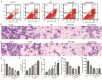
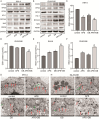
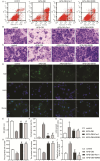
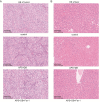
Results: The IC50 of APS and DB in IHH-4 cells were 153.9 µg/mL and 41.2 µM, respectively, while they were 728.0 µg/mL and 22.74 µM in GLAG-66 cells. Combination of APS and DB enhanced the anti-cancer role of DB with increased cell apoptosis and LDH release, and weakened cell growth, migration and invasion capacities. Interestingly, the combination of these two drugs significantly alleviated the liver injury induced by DB. In mechanism, we found that APS combined with DB treatment triggered the increase of MDA level while decreased GSH level, and deteriorated mitochondria damage. Inhibition of ferroptosis impaired the anti-PTC role of APS combined with DB with no influencing on liver injury both in vivo and in vitro.
Conclusions: In conclusion, our study shows the combined therapy strategy of APS and DB regimen achieves better anti-cancer response through increasing MDA level while decreasing GSH level. Importantly, the combined therapy of APS and DB significantly decreased the liver toxicity induced by DB. These findings suggest that APS combined DB is a potential therapeutic strategy for BRAFmut PTC with high efficacy and low liver toxicity.
Keywords: BRAF mut papillary thyroid cancer; Astragalus polysaccharide; Diosbulbin B; Ferroptosis; Liver injury.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the institutional guidelines and approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Approval no 20240221011). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
- 2023JD104/Shenzhen Bao'an District Science, Technology and Innovation Bureau, Medical and Health Basic Research Project
- BAYXH2024020/Health and Medical Scientific Research Project of Shenzhen Bao'an Medical Association
- YNXM2024020/Shenzhen Bao'an District High Quality Development Project of Public Hospitals
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

