Impact of GLP-1 receptor agonist-based therapies on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with CKD
- PMID: 40605083
- PMCID: PMC12220177
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-025-01831-4
Impact of GLP-1 receptor agonist-based therapies on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetic and non-diabetic patients with CKD
Abstract
Background: The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists-based therapies on cardiovascular and renal outcomes has not been systematically reviewed across baseline kidney function groups. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (RAs) in patients with and without chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods: We performed a PubMed/Medline search of randomized, placebo-controlled, event-driven outcome trials of GLP-1 RAs versus placebo in patients with and without diabetes from inception to January 2025. CKD was defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 60 ml/min/1.73m2. The primary outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Secondary outcomes included hospitalization for heart failure, CKD progression, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. The relative risk (RR) was estimated using a random-effects model.
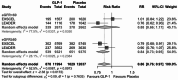
Results: Nine RCTs were included with a total of 75,088 patients, including 17,568 with eGFR < 60 ml/min/1.73m2. Use of an GLP-1 RA in patients with CKD was associated with a lower incidence of MACE (RR 0.84; 95% CI 0.74-0.95; P 0.006) and of CKD progression (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.77-0.94; P 0.002), compared with placebo. There was no differential treatment effect of GLP-1 RA on these endpoints by CKD status at baseline.
Conclusions: GLP-1 RAs offer substantial cardiovascular and renal protection in patients with CKD. These findings support their use in CKD patients and confirms that these therapies may be continued as kidney function declines.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

