"Early, rapid, aggressive": when strategic interactions between governments, opposition, and lobbies can hinder effective responses to epidemics
- PMID: 40605859
- PMCID: PMC12213477
- DOI: 10.3389/fepid.2025.1593883
"Early, rapid, aggressive": when strategic interactions between governments, opposition, and lobbies can hinder effective responses to epidemics
Abstract
Background: Two critical factors in the success of the response to a threatening epidemic outbreak are the degree of responsibility of the main political actors involved in the response and the population compliance to the proposed measures. The Behavioural epidemiology literature has focused on the latter factor but largely disregarded the former. The multiple failures in COVID-19 control and the lack of consensus that still surround the main response options (i.e., the elimination-suppression-mitigation trichotomy) highlight the importance of considering the political layer in preparedness activities.
Methods: We integrate a simple transmission model into a game-theoretic framework for the interaction between the main political actors involved in the response, namely a government, its opposition and lobbies. The aim is to provide a conceptual framework allowing one to identify the political factors promoting a timely and effective response.
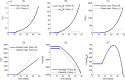
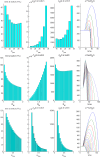
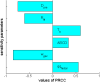
Results: Low degrees of responsibility (i.e., prioritizing consensus over health protection) of political agents can delay or de-potentiate the response until when epidemic growth eventually overtakes the agents' payoffs, thereby forcing them to switch towards the higher degree of responsibility needed to promote an adequate response. When both the government and the opposition are only "partly" responsible, a stall in the response decision-making process likely arises, further delaying the response. Policy and epidemiological parameters amplifying the response delay are ranked by a sensitivity analysis.
Conclusions: Promoting a high degree of responsibility of political actors and lobbies during emergency situations should be a key target of preparedness. Therefore, future pandemic plans should also include, beyond technical indications, ethical statements "guiding" political entities to cooperation.
Keywords: effective responses to epidemics; game theory; political consensus vs. health protection; political responsibility; preparedness; social distancing; transmission models.
© 2025 Carrozzo Magli, Bauch, d'Onofrio and Manfredi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
EORTC guidelines for the use of erythropoietic proteins in anaemic patients with cancer: 2006 update.Eur J Cancer. 2007 Jan;43(2):258-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2006.10.014. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Eur J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17182241
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manfredi P, d’Onofrio A. Modeling the Interplay Between Human Behavior and the Spread of Infectious Diseases. New York: Springer; (2013).
-
- Wang Z, Bauch CT, Bhattacharyya S, d'Onofrio A, Manfredi P, Perc M, et al. Statistical physics of vaccination. Phys Rep. (2016) 664:1–113. 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.10.006 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

