Liver function dynamics in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemoembolization
- PMID: 40606002
- PMCID: PMC12214317
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359251347363
Liver function dynamics in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors with or without transarterial chemoembolization
Abstract
Background: The efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) antibody/tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been established. However, it remains unclear whether the addition of TACE to systemic therapies exacerbates liver function deterioration and increases mortality risk.
Objectives: To assess liver function changes and their impact on prognosis in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treated with ICIs and anti-VEGF antibody/TKIs with or without TACE as first-line therapy.
Design: This is a real-world retrospective cohort study.
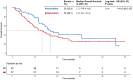
Methods: Patients with advanced HCC treated with TACE combined with ICIs and anti-VEGF antibody/TKIs (TACE-ICI-VEGF) or ICIs and anti-VEGF antibody/TKIs alone (ICI-VEGF) from January 2018 to June 2024 were retrospectively included. The primary outcomes were changes in albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score and time to deterioration (TTD) of liver function. The secondary outcomes included overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and the relationship between TTD and prognosis.
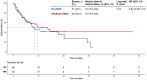
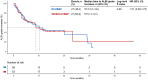
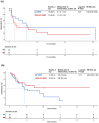
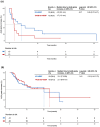
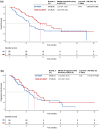
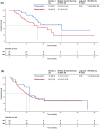
Results: A total of 111 patients were included, with 54 and 57 patients receiving TACE-ICI-VEGF and ICI-VEGF, respectively. Changes in ALBI score were similar between groups (difference in least squares mean, -0.075; 95% confidence interval (CI): -0.298 to 0.148). TTD was also comparable (median for TACE-ICI-VEGF 9.7 months vs. ICI-VEGF 8.5 months; hazard ratio (HR) = 1.19 (95% CI: 0.71-2.01); p = 0.512). TACE-ICI-VEGF group demonstrated a significantly improved median OS (18.3 vs. 11.8 months; HR = 0.60 (95% CI: 0.37-0.98); p = 0.041) and a trend toward prolonged median PFS (14.7 vs. 11.2 months; HR = 0.76 (95% CI: 0.47-1.25); p = 0.278). Patients with liver function deterioration had an increased risk of mortality (median OS: 13.2 vs. 17.0 months; HR = 1.44 (95% CI: 0.88-2.35); p = 0.139).
Conclusion: TACE combined with ICIs plus anti-VEGF antibodies/TKIs as first-line treatment generally did not adversely affect liver function. Liver function deterioration was associated with an increased risk of mortality.
Keywords: albumin-bilirubin score; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver function; systemic therapies; transarterial chemoembolization.
© The Author(s), 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2024; 74: 229–263. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021; 7: 6. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Villanueva A, Marrero JA, et al. Trial design and endpoints in hepatocellular carcinoma: AASLD consensus conference. Hepatology 2021; 73(Suppl. 1): 158–191. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

