Comparison of Telomere Structure in Eukaryotes
- PMID: 40606259
- PMCID: PMC12214437
- DOI: 10.32592/ARI.2024.79.6.1365
Comparison of Telomere Structure in Eukaryotes
Abstract
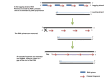
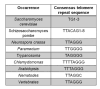
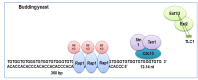
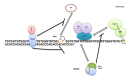
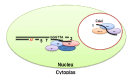
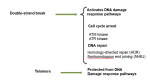
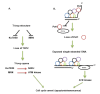
Telomeres are DNA-protein complexes that are located at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. The fusion of broken chromosome ends is prevented by the presence of telomeres, which act to inhibit this process. This specific function of telomeres serves to distinguish normal chromosome ends from double-stranded breaks in DNA. Telomeres contain a series of short, repeated sequences arranged in a tandem array. The number of repeats varies between different organisms, with a range of 20 to 1,000 repeats being typical. A G-rich strand is replicated by lagging strand synthesis, which creates a 3' overhang. In addition, a complementary C-rich strand is replicated by leading strand synthesis. The objective of this study is to undertake a comparative analysis of the structure of telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Saccharomyces pombe and mammals. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the Rap1 protein binds to the double-stranded telomeric sequences, as well as to the Rif1 and Rif2 proteins, which regulate telomere length. Cdc13 and the Cdc13-interacting factors Ten1 and Stn1 bind to the single-stranded overhang. In Saccharomyces pombe telomeres, Taz1 binds to the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), and Rap1 and Rif1 also bind to the ds region via Taz1. Pot1 interacts with Tpz1, forming a complex that binds to the 3' overhang. The protein Poz1 serves to connect the dsDNA binding complex, comprising Taz1 and Rap1, to the ssDNA binding complex, which includes Pot1 and Tpz1. Furthermore, Ccq1 interacts with Tpz1 and facilitates the recruitment of telomerase. The Stn1/Ten1 complex exhibits a binding affinity for a single-stranded telomere. In mammalian telomeres, the shelterin complex that binds double-stranded telomeric DNA is composed of six subunits. The double-stranded telomeric DNA is bound by TRF1 and TRF2. TPP1 and POT1 are capable of binding single-stranded DNA. TIN2 serves to connect the dsDNA binding complex TRF1/TRF2 to the ssDNA binding complex POT1/TPP1. Rap1 binds to the telomere by interacting with TRF1 and TRF2. Moreover, this study will address the regulation and comparison of the shelterin complex. Additionally, in mammals, the activation of DNA damage response pathways is necessary when double-strand DNA is broken. This, in turn, elucidates the specific repair pathways that are employed. We conclude by discussing the T-loop structure, as telomeres in several species have been shown to fold back into a structure called a T-loop, which is believed to mediate telomere protection.
Keywords: Shelterin; T-Loop Structure; Telomere.
Conflict of interest statement
In the interest of transparency and to ensure the integrity of the research process, the corresponding author on behalf of all authors states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Caenorhabditis elegans telomere-binding proteins TEBP-1 and TEBP-2 adapt the Myb module to dimerize and bind telomeric DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 16;121(16):e2316651121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2316651121. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38588418 Free PMC article.
-
Ccq1 restrains Mre11-mediated degradation to distinguish short telomeres from double-strand breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 24;52(7):3722-3739. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae044. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38321948 Free PMC article.
-
The canonical RPA complex interacts with Est3 to regulate yeast telomerase activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Feb 18;122(7):e2419309122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2419309122. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39913192 Free PMC article.
-
Structural biology of telomeres and telomerase.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Jan;77(1):61-79. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03369-x. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31728577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
POT1-TPP1 telomere length regulation and disease.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Jul 3;18:1939-1946. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.06.040. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32774788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blackburn E, Szostak J. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annual review of biochemistry. 1984;53(1):163–94. - PubMed
-
- Levy MZ, Allsopp RC, Futcher AB, Greider CW, Harley CB. Telomere end-replication problem and cell aging. Journal of molecular biology. 1992;225(4):951–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
