Comparison of tegoprazan-based and proton pump inhibitor-based regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 40606460
- PMCID: PMC12215699
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1580203
Comparison of tegoprazan-based and proton pump inhibitor-based regimens for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Background and aim: Tegoprazan (TEG) is a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB) that provides long-lasting acid-suppressing effects. The role of TEG-based Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication regimens in comparison to proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-based regimens requires further investigation.
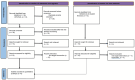
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search across multiple databases. Studies comparing H. pylori eradication rates, adverse events (AEs), and compliance between TEG-based and PPI-based regimens were included. Statistical analyses were performed using RevMan 5.4.
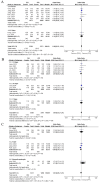
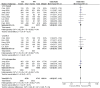
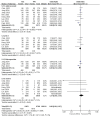
Results: A total of eight studies involving 4,640 patients were included. Based on intention-to-treat (ITT) analyses, the overall eradication rate (78.6% vs. 76.6%; odds ratio [OR] = 1.08, 95% CI: 0.93-1.24; p = 0.31, I 2 = 0%) and compliance (97.8% vs. 97.8%; OR = 1.16, 95% CI: 0.54-2.50; p = 0.33, I 2 = 13%) were comparable between the TEG and PPI groups. The AE rate of TEG-based regimens was significantly lower than that of PPI-based regimens (30.8% vs. 34.9%; OR = 0.88; 95% CI: 0.78-1.00; p = 0.04, I 2 = 67%), although this difference was not significant in the randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The subgroup analyses showed higher eradication rates in studies conducted in China, those with treatment durations of 10 or 14 days, and those using dual or bismuth quadruple regimens. However, the treatment regimens did not significantly influence eradication rates within any subgroup.
Conclusion: TEG-based H. pylori eradication treatment demonstrated similar eradication rates, compliance, and safety to PPI-based regimens.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024629665.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; adverse events; compliance; eradication; proton pump inhibitor; tegoprazan.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Li, Li, Deng, Xu, Chen and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sequential versus standard triple first-line therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 28;2016(6):CD009034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009034.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27351542 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Potassium-Competitive Acid Blockers and Proton Pump Inhibitors for First-Line Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Helicobacter. 2024 Nov-Dec;29(6):e13150. doi: 10.1111/hel.13150. Helicobacter. 2024. PMID: 39508303
-
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Potassium-Competitive Acid Blocker- and Proton Pump Inhibitor-Based Bismuth Quadruple Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Network Meta-Analysis.Gastro Hep Adv. 2025 May 16;4(9):100705. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100705. eCollection 2025. Gastro Hep Adv. 2025. PMID: 40761703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of tegoprazan and proton pump inhibitors for first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication: a systematic review with meta-analysis.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2025 Feb-Apr;23(2-4):227-233. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2025.2459722. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2025. PMID: 39862182
-
Tailored therapy guided by genotypic resistance from gastric mucosa samples in the first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 26;18:17562848251348826. doi: 10.1177/17562848251348826. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40583969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, Rokkas T, Gisbert JP, Liou JM, Schulz C, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut. (2022) 71:1724–62. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327745 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

