Life's Crucial 9 score and chronic kidney disease: insights from NHANES 2005-2018 and the mediating role of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress
- PMID: 40606462
- PMCID: PMC12213831
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1605931
Life's Crucial 9 score and chronic kidney disease: insights from NHANES 2005-2018 and the mediating role of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a growing global health burden, closely linked to metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors. Life's Crucial 9 (LC9) is a novel health assessment tool that expands upon Life's Essential 8 (LE8) by incorporating mental health (depression) as a key component. This study aimed to investigate the association between LC9 and CKD, compare its predictive value with LE8, and explore potential mediating mechanisms.
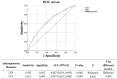
Methods: This study analyzed data from 16,431 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2018. Logistic regression models were used to assess the association between LC9 and CKD, with comparisons to LE8. Restricted cubic spline models were applied to explore potential nonlinear relationships. Mediation analysis was conducted to evaluate whether systemic inflammation and oxidative stress mediated the association between LC9 and CKD. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to compare the predictive performance of LC9 and LE8 for CKD risk.
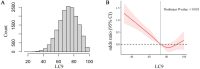
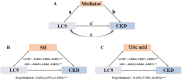
Results: Higher LC9 scores were significantly associated with a lower risk of CKD in both continuous and quartile-based analyses. A nonlinear relationship was observed between LC9 and CKD risk (P for nonlinearity < 0.001). Mediation analysis indicated that systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and uric acid partially mediated the association between LC9 and CKD, with mediation proportions of 3.32 and 11.13%, respectively. ROC analysis showed that LC9 and LE8 had comparable predictive abilities for CKD.
Conclusion: Higher LC9 scores are associated with a reduced risk of CKD, with systemic inflammation and uric acid levels partially mediating this relationship. These findings highlight the importance of comprehensive lifestyle and mental health interventions in CKD prevention and management.
Keywords: CKD; LC9; LE8; NHANES; mediation analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Qin, Yang, Wang, He, Dong, Ren and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress and inflammation mediate the association between Life's Crucial 9 and biological ageing: A secondary analysis of two observational studies.J Nutr Health Aging. 2025 Jul;29(7):100575. doi: 10.1016/j.jnha.2025.100575. Epub 2025 May 6. J Nutr Health Aging. 2025. PMID: 40334364 Free PMC article.
-
The curvilinear associations between Life's Crucial 9 and frailty: cross-sectional study of NHANES 2003 - 2023.Front Aging. 2025 Jun 6;6:1528338. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1528338. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40547965 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Life's Crucial 9 and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: the mediating role of neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 6;12:1549089. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1549089. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40547368 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D, Mozaffarian D, Appel LJ, Van Horn L, et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association's strategic impact goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. (2010) 121:586–613. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.109.192703, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hasbani NR, Ligthart S, Brown MR, Heath AS, Bebo A, Ashley KE, et al. American Heart Association's life's simple 7: lifestyle recommendations, polygenic risk, and lifetime risk of coronary heart disease. Circulation. (2022) 145:808–18. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.121.053730, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

