Three-year impact of COVID-19 pandemic on hospitalized twin pregnancies: evaluation of characteristics and changes in antibiotic prescribing
- PMID: 40606471
- PMCID: PMC12213898
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1546013
Three-year impact of COVID-19 pandemic on hospitalized twin pregnancies: evaluation of characteristics and changes in antibiotic prescribing
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted healthcare systems worldwide, including obstetric care. However, the long-term effects on twin pregnancies remain unclear. This study investigates the impact of COVID-19 on the clinical characteristics and antibiotic prescribing patterns in hospitalized twin pregnancies.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted at Women and Children's Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China, involving 3,827 twin pregnancies with live deliveries between 1 January 2017 and 31 December 2022. The pre-pandemic group included 1,707 patients, and the pandemic group included 2,120. Sociodemographic and clinical data were analyzed using general linear models with SPSS and R software.
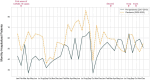
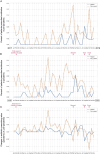
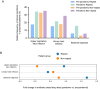
Results: During the pandemic, twin pregnancy admissions increased by 24.19%. Patients in the pandemic group have less gestational weight gain (17.00 vs. 16.08 kg, P < 0.001), had higher rates of assisted reproductive technology use (73.2% vs. 68.7%, P = 0.002), and experienced more complications. Neonates showed higher rates of pneumonia (5.7% vs. 3.8%, P < 0.001) and NICU admissions (43.7% vs. 13.9%, P < 0.001). Longer hospital stays were observed in the pandemic group (P = 0.004). Antibiotic prescriptions, especially non-repeat prescriptions, increased for older patients, those with higher BMI, and premature deliveries. The rate of repeated antibiotic prescriptions for bacterial vaginosis increased 1.68 times.
Conclusion: COVID-19 influenced twin pregnancy admissions, clinical characteristics, and antibiotic use. The study highlights the need for rational antibiotic use and improved healthcare resource management in future crises.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; antibiotic prescribing; clinical characteristics; retrospective cohort study; twin pregnancies.
Copyright © 2025 Cai, Liu, Zhi, Tang, Wang, Lan, Wen, Luo, Wang, Sheng and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Buch-Vicente B, Acosta-Rodriguez JM, Sanchez-Sanchez ME, González-García N, Garcia-Ullan L, de la Iglesia-Larrad JI, et al. Coping strategies used by health-care workers during the SARS-COV2 crisis. A real-world analysis. Psychiatry Res. (2022) 317:114915. 10.1016/j.psychres.2022.114915 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

