Mutation of beta-tubulin 4B gene (TUBB4B) causes autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa with sensorineural hearing loss in a multigenerational family
- PMID: 40606475
- PMCID: PMC12221308
Mutation of beta-tubulin 4B gene (TUBB4B) causes autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa with sensorineural hearing loss in a multigenerational family
Abstract
Purpose: Members of a multigenerational Canadian family presented to an inherited retinal degeneration (IRD) clinic with retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and sensorineural hearing loss, reminiscent of an Usher syndrome phenotype. Biallelic disease-causing variants in the known Usher syndrome genes were not identified. Therefore, we enrolled further family members in this study and examined whether other IRD gene variants could explain the phenotype in the family.
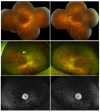
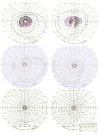
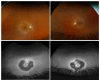
Methods: Family members underwent a comprehensive ophthalmic examination, including best-corrected visual acuity, direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy, fundus photography, visual field testing, spectral-domain optical coherence tomography, audiological examination, and genetic testing. Some patients also had autofluorescence imaging. Loss-of-function testing was initiated by antisense morpholino knockdown of tubb4b in zebrafish.
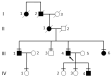
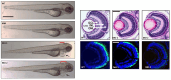
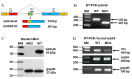
Results: Multimodal clinical testing in affected patients revealed an autosomal dominant late-onset presentation of RP associated with progressive, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss that occurred in the second to third decades of life with no vestibular involvement. Panel-based genetic testing revealed a heterozygous c.1168C>T, p.Arg390Trp variant in the beta-tubulin 4B gene (TUBB4B) only in affected family members. Based on in silico analysis, segregation analysis through the family, and literature evaluation, this variant is likely to be the disease-causing variant inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. We searched our local database of ~1,000 patients with IRD, and no other TUBB4B variants were identified, confirming this is a rare disease variant. Knockdown of tubb4b in zebrafish revealed cone and rod photoreceptor abnormalities in the retina and hydrocephalus in the developing brain, resulting in early larval lethality.
Conclusions: For the first time, we describe a multigenerational family with a TUBB4B gene variant p.(Arg390Trp) segregating with deaf-blindness, establishing autosomal dominant inheritance. This further confirms that the Arg390 codon is a mutation hotspot. We also expand the range of phenotypes seen with the p.(Arg390Trp) TUBB4B gene variant to include typical RP as well as a milder, pericentral RP. Furthermore, our studies suggest there is conservation of TUBB4B ciliary function between zebrafish and humans, making zebrafish a better model system for studying vision loss than the mouse model.
Copyright © 2025 Molecular Vision.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of 171 Patients with Syndromic Inherited Retinal Diseases Highlights the Importance of Genetic Testing for Accurate Clinical Diagnosis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;16(7):745. doi: 10.3390/genes16070745. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725402 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of two hotspot codons in the TUBB4B gene and associated phenotypes.Sci Rep. 2024 May 8;14(1):10551. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61019-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38719929 Free PMC article.
-
Variants in the AGBL5 gene are responsible for autosomal recessive Retinitis pigmentosa with hearing loss.Eur J Hum Genet. 2025 Jun;33(6):727-737. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01768-8. Epub 2024 Dec 13. Eur J Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 39672920 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical phenotype and genotypic analysis of a four-generation Chinese pedigree affected with Stickler syndrome and a literature review].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 10;42(6):684-690. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20250418-00235. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40763965 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Dammeyer J. Prevalence and aetiology of congenitally deafblind people in Denmark. Int J Audiol. 2010;49:76–82. - PubMed
-
- Yazigi A, De Pecoulas AE, Vauloup-Fellous C, Grangeot-Keros L, Ayoubi J-M, Picone O. Fetal and neonatal abnormalities due to congenital rubella syndrome: a review of literature. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;30:274–8. - PubMed
-
- Oldenski R. Cogan syndrome: autoimmune-mediated audiovestibular symptoms and ocular inflammation. J Am Board Fam Pract. 1993;6:577–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

