Escaping endogenous miRNA post-transcriptional silencing of JrGRF4b enhanced transformation efficiency in woody plants
- PMID: 40606477
- PMCID: PMC12213585
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1629166
Escaping endogenous miRNA post-transcriptional silencing of JrGRF4b enhanced transformation efficiency in woody plants
Abstract
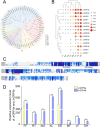
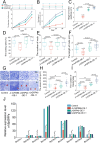
The stable expression of transgenes was critically influenced by post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in transgenic plants. In this study, we investigated the influence of endogenous miRNA-mediated silencing on heterologous gene expression by introducing walnut (Juglans regia L.)-derived Growth-Regulating Factors 4 (JrGRF4b), disrupting miR396-mediated silencing of replace-JrGRF4b (rJrGRF4b), and Jr-miR396a into birch (Betula platyphylla Suk.). While JrGRF4b overexpression showed no significant improvement in transformation efficiency due to Bp-miR396-mediated suppression, transgenic lines expressing rJrGRF4b exhibited a 2.53% increase in transformation efficiency, along with significantly enhanced callus diameter, adventitious bud height, root elongation, cellular expansion, and shoot primordia proliferation compared to control (**p<0.01). In contrast, Jr-miR396a-overexpressing plants displayed growth inhibition through suppression of endogenous BpGRFs. The results showed that escaping endogenous miRNA regulation by targeted site modification of rJrGRF4b significantly improved transgene performance in woody plants. Thus, comprehensive evaluation of post-transcriptional epigenetic regulation between transgenes and endogenous miRNAs in recipient plants was demonstrated to be important, and targeted escape from such miRNA-mediated suppression was shown to ensure stable and high-efficiency transgene expression.
Keywords: MiR396; birch; growth-regulating factors; post-transcriptional regulatory; transgene; walnut.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Pan, Wu, Zheng and Pei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Baucher M., Moussawi J., Vandeputte O. M., Monteyne D., Mol A., Pérez-Morga D., et al. (2013). A role for the miR396/GRF network in specification of organ type during flower development, as supported by ectopic expression of P opulus trichocarpa miR396c in transgenic tobacco. Plant Biol. 15, 892–898. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2012.00696.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

