Integrated miRNAome, transcriptome, and degradome analyses reveal the role of miRNA-mRNA modules in the biosynthesis of oridonin in Isodon rubescens
- PMID: 40606481
- PMCID: PMC12213554
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1566354
Integrated miRNAome, transcriptome, and degradome analyses reveal the role of miRNA-mRNA modules in the biosynthesis of oridonin in Isodon rubescens
Abstract
Introduction: Isodon rubescens contains many bioactive diterpenoids, especially oridonin, which are used both as medicines and drinks. However, the structure and content of the diterpenoids in I. rubescens vary greatly in response to different ecological environments. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a pivotal role in the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites; but their roles in I. rubescens are obscure.
Methods: This research involved conducting miRNAome, transcriptome, and degradome sequencing analysis of three ecotypes of I. rubescens. Furthermore, the regulation of two candidate miRNA-mRNA modules was validated through a dual-luciferase reporter system.
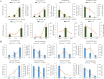
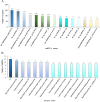
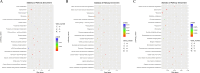
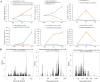
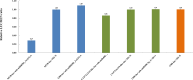
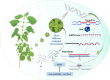
Results: In this study, a total of 1634 miRNAs were identified from 9 miRNAome libraries of three I. rubescens ecotypes, which contained various contents of oridonin, lasiodonin, and rosthorin A. Furthermore, 99 DEMs and 8180 DEGs were obtained across three I. rubescens ecotypes, and the expressions of selected DEMs and DEGs were verified via reverse transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). A total of 8928 miRNA-mRNAs networks were identified by degradome analysis, and 23 miRNA-mRNA modules were enriched in the terpenoid biosynthesis pathway. Additionally, 92 negatively correlated DEM‒DEG modules were identified through integrated miRNAome, transcriptome, and degradome analyses, ath-miR858b_1ss21GA‒MYB and ath-miR408-3p_L-1R+1‒CYP72A219 modules were likely involved in oridonin biosynthesis in I. rubescens. Furthermore, the negative regulation of ath-miR858b_1ss21GA targeted MYB was validated through a dual-luciferase reporter system.
Discussion: This study revealed that Ath-miR858b_1ss21GA could repress MYB transcription, potentially downregulating the specific genes involved in the biosynthesis of oridonin and reducing oridonin accumulation in I. rubescens.
Keywords: Isodon rubescens; dual-luciferase reporter assay; miR858b_1ss21GA-MYB module; multiomics analysis; oridonin biosynthesis.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Zhang, Guo, Xu, Wang and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multi-omics analysis of small RNA, transcriptome, and degradome to identify putative miRNAs linked to MeJA regulated and oridonin biosynthesis in Isodon rubescens.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Feb;258(Pt 2):129123. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.129123. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38163496
-
Identification of MicroRNAs and Their Targets That Respond to Powdery Mildew Infection in Cucumber by Small RNA and Degradome Sequencing.Front Genet. 2020 Mar 26;11:246. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00246. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32273882 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Deciphering Shared Gene Signatures and Immune Infiltration Characteristics Between Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Preeclampsia by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis and Machine Learning.Reprod Sci. 2025 Jun;32(6):1886-1904. doi: 10.1007/s43032-025-01847-1. Epub 2025 May 15. Reprod Sci. 2025. PMID: 40374866
-
Interventions for the management of malignant pleural effusions: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 8;2016(5):CD010529. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010529.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 21;4:CD010529. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010529.pub3. PMID: 27155783 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

