Effects of a single tDCS with mirror therapy stimulation on hand function in healthy individuals
- PMID: 40606492
- PMCID: PMC12213558
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1607022
Effects of a single tDCS with mirror therapy stimulation on hand function in healthy individuals
Abstract
Introduction: Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a non-invasive neuromodulatory technique that has garnered significant interest for its ability to modulate cortical excitability and brain function. The technique involves the application of a weak electrical current through electrodes placed on the scalp, which influences neuronal membrane potential and alters synaptic plasticity.
Methods: The following research hypotheses were defined: (1) a single tDCS stimulation of the motor cortex on the left side in combination with mirror therapy (MT) improves the function of the right hand which is dominant; and (2) a single stimulation in combination with MT for the dominant hand (right hand) also improves the function of the non-dominant hand (left hand). A total of 106 subjects aged 51.5 ± 12.02 participated in the study, including 63 women and 43 men. We used tests for assessment before and after tDCS stimulation: Tapping Tablet, Reaction Test on a tablet, Nine Hole Peg Test (NHPT), exercises for dominant hands, tDCS stimulation with MT.
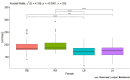
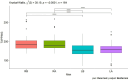
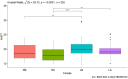
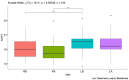
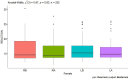
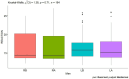
Results: The obtained results of this conducted study, although preliminary, seem to indicate that in each of the analyzed age groups in men and women, a single tDCS stimulation in combination with MT directly improved the function of the dominant hand and indirectly improved the function of the non-dominant hand.
Discussion: The use of tDCS stimulation appears promising to improve hand function.
Keywords: hand; healthy people; mirror therapy; tDCS stimulation; test.
Copyright © 2025 Wójcik, Vlček, Siatkowski and Grünerová-Lippertová.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agboada D., Mosayebi-Samani M., Kuo M. F., Nitsche M. A. (2020). Induction of long-term potentiation-like plasticity in the primary motor cortex with repeated anodal transcranial direct current stimulation - Better effects with intensified protocols? Brain Stimul. 13 987–997. 10.1016/j.brs.2020.04.009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

