Tissue nanotransfection and cellular reprogramming in regenerative medicine and antimicrobial dynamics
- PMID: 40606909
- PMCID: PMC12213499
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1558735
Tissue nanotransfection and cellular reprogramming in regenerative medicine and antimicrobial dynamics
Abstract
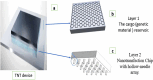
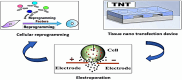
Tissue nanotransfection (TNT) is a novel, non-viral nanotechnology platform that enables in vivo gene delivery and direct cellular reprogramming through localized nanoelectroporation. This review synthesizes current advancements in TNT, outlining its device architecture, electroporation principles, and optimized delivery of genetic cargo, including plasmid DNA, mRNA, and CRISPR/Cas9 components. The mechanisms underlying TNT-mediated cellular reprogramming are critically evaluated, including transcriptional activation, epigenetic remodeling, and metabolic shifts, across three major reprogramming strategies-induced pluripotency, direct lineage conversion, and partial cellular rejuvenation. TNT demonstrates transformative therapeutic potential in diverse biomedical applications, including tissue regeneration, ischemia repair, wound healing, immunotherapy, and antimicrobial therapy. This review highlights TNT's unique advantages over traditional gene delivery systems, namely, its high specificity, non-integrative approach, and minimal cytotoxicity, while also addressing existing limitations such as phenotypic stability and scalability. By integrating emerging data and identifying key translation challenges, this work positions TNT as a conceptual and technological advance in regenerative medicine and targeted gene therapy, offering a roadmap for future research and clinical implementation.
Keywords: antimicrobial; cellular reprogramming; regenerative medicine; tissue nanotransfection; wound healing.
Copyright © 2025 Shakra.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emergence of snail mucus as a multifunctional biogenic material for biomedical applications.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jun 15;200:21-46. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.05.006. Epub 2025 May 2. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40319989 Review.
-
Tissue Nanotransfection Silicon Chip and Related Electroporation-Based Technologies for In Vivo Tissue Reprogramming.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;14(2):217. doi: 10.3390/nano14020217. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38276735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ethical Implications of Tissue Engineering for Regenerative Purposes: A Systematic Review.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023 Apr;29(2):167-187. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2022.0033. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023. PMID: 36112697 Free PMC article.
-
AI-Driven Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery: Mining and Generation.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Jun 17;58(12):1831-1846. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00594. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 40459283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct Lineage Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Functional Keratinocyte-Like Cells via BMI1 and FGFR2b for Diabetic Wound Repair.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s12015-025-10929-1. Online ahead of print. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025. PMID: 40579673
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

