Diagnostic performance of Liver FibraChek Dx©, a blood-based test for the non-invasive detection of liver cirrhosis and cancer
- PMID: 40606917
- PMCID: PMC12210174
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.106481
Diagnostic performance of Liver FibraChek Dx©, a blood-based test for the non-invasive detection of liver cirrhosis and cancer
Abstract
Background: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), hepatic fibrosis, and cirrhosis are major risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), yet current blood-based diagnostic assays lack sufficient accuracy for routine clinical use. Identifying a non-invasive molecular signature that accurately detects liver disease could improve early diagnosis and monitoring. We hypothesized that the Liver FibraChek Dx© serum assay could discriminate MASLD and HCC from healthy controls using a multiplex biomarker-based algorithm.
Aim: To evaluate the diagnostic performance of the Liver FibraChek Dx© assay for detecting MASLD and HCC.
Methods: This was a prospective, single-center study conducted in a United States tertiary care setting. Serum samples were collected from 45 participants (14 MASLD, 19 HCC, 12 healthy controls) with liver histology confirmed by biopsy. The Liver FibraChek Dx© algorithm integrates weighted values of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, taurocholic acid, L-tyrosine, platelet count, and patient age to generate a risk score. Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to assess associations with histologic diagnosis, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves quantified diagnostic performance.
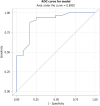
Results: Liver FibraChek Dx© risk scores were significantly elevated in MASLD and HCC compared to controls (median: 6.92 ± 3.86 vs 3.61 ± 1.67, P < 0.001). The area under the ROC curve was 0.890 (95%CI: 0.776-1.000) for distinguishing diseased from healthy individuals. Sensitivity was 93.9%, specificity 75.0%, positive predictive value 91.1%, negative predictive value 81.8%, and overall accuracy 88.9%.
Conclusion: The Liver FibraChek Dx© assay accurately detects liver disease and shows promise as a non-invasive tool for diagnosing and monitoring MASLD and HCC.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cirrhosis; Fibrosis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; High pressure liquid chromatography; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Metabolomics; Multiplex; Peripheral blood.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Charles J Rosser is an officer at Nonagen Bioscience Corporation (Los Angeles, CA, United States), which has patent interests in and development rights to the Liver FibraChek Dx© assay. The remaining authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose, financial or otherwise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Platelet count, spleen length, and platelet count-to-spleen length ratio for the diagnosis of oesophageal varices in people with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 26;4(4):CD008759. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008759.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28444987 Free PMC article.
-
Blood biomarkers for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 1;2016(5):CD012179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012179. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27132058 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen stiffness measurement by vibration-controlled transient elastography at 100 Hz for non-invasive predicted diagnosis of clinically significant portal hypertension in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease: a modelling study.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Dec;9(12):1111-1120. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(24)00234-6. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39326431
-
Non-invasive diagnostic assessment tools for the detection of liver fibrosis in patients with suspected alcohol-related liver disease: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(4):1-174. doi: 10.3310/hta16040. Health Technol Assess. 2012. PMID: 22333291 Free PMC article.
-
The serum uric acid to apolipoprotein A1 ratio is independently correlated with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: findings from a single national metabolic management center cohort.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 4;16:1619003. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1619003. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40535329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kisseleva T, Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18:151–166. - PubMed
-
- Lambrecht J, Verhulst S, Mannaerts I, Reynaert H, van Grunsven LA. Prospects in non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis: Liquid biopsy as the future gold standard? Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864:1024–1036. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

