Hope on the horizon: Emerging therapies for hepatitis D
- PMID: 40606936
- PMCID: PMC12210157
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.107963
Hope on the horizon: Emerging therapies for hepatitis D
Abstract
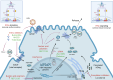
Current treatment options for hepatitis D are limited, with pegylated interferon-alpha (PEG-IFNα) being the only therapy available in the Asia-Pacific region. However, PEG-IFNα has limited efficacy and significant side effects. Pegylated interferon lambda acts on interferon-lambda (Type III) receptors predominantly expressed in hepatocytes. In 2023, bulevirtide was approved in the European Union and Russia for treating chronic hepatitis D. This drug works by binding to and inhibiting the sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide receptor on liver cells, which is the primary entry point for the virus. Recently, several new drugs have entered various stages of development, offering hope for improved hepatitis D virus (HDV) management. Two more viral entry inhibitors are HH003 and tobevibart. Other agents include nucleic acid polymers (REP 2139-Mg), prenylation inhibitors (lonafarnib), and RNA interference-based therapies (elebsiran). Emerging trials are now considering combination therapies, such as SOLSTICE, a Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating tobevibart alone or combined with elebsiran. The combination dosed monthly achieved > 50% virologic and biochemical response at 24 weeks of therapy. The efficacy and safety of these drugs will further be evaluated in ECLIPSE 1, 2, and 3 trials. With these new treatments on the horizon, the prospects for improved HDV patient outcomes are promising.
Keywords: Bulevirtide; Elebsiran; Hepatitis B; Hepatitis D; Lonafarnib; Nucleic acid polymers; Pegylated interferon; Tobevibart; Treatment.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Abbas Z contributed patients to the D-LIVR study. He is the principal investigator from his site for HHoo3, ECLIPSE 1, and 3 studies mentioned in the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

