Retrospective analysis of HIV-associated lymphomas: insights from a single Romanian center over 15 years
- PMID: 40606992
- PMCID: PMC12213895
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1569433
Retrospective analysis of HIV-associated lymphomas: insights from a single Romanian center over 15 years
Abstract
Introduction: Lymphoma is a significant cause of mortality among people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLWH). The objective of our study was to assess the characteristics of lymphomas in PLWH in a single center from the southeast of Romania.
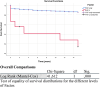
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the prevalence and clinical and demographic characteristics of patients with lymphoma associated with HIV/AIDS monitored over a period of 15 years. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to estimate survival rates and evaluate the risk of mortality in lymphoma patients.
Results: Among the 476 new cases of HIV/AIDS registered, 9 cases of lymphoma were identified, representing a prevalence of 1.89%. Overall mortality was 13.6%, with lymphoma contributing to 10.76% of HIV/AIDS-related deaths. The average age at lymphoma diagnosis was 37 years, with most patients being men and smokers with sexually transmitted HIV. Common coinfections included hepatitis B virus (HBV) and tuberculosis. Advanced-stage disease (Ann Arbor stage IV) and type B clinical symptoms were present in half of the cases. Oncological treatment was provided in 5 cases, achieving a survival rate of 30%.
Conclusions: The high mortality highlights the need for early diagnosis and an integrated therapeutic approach to improve the prognosis of patients with HIV-associated lymphomas.
Keywords: AIDS; HIV; antiretroviral treatment; lymphoma; non-AIDS co-morbidities; opportunistic infections.
Copyright © 2025 Padurariu-Covit, Chiscop, Gutu, Arbune, Niculet and Arbune.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO . The urgency of now: AIDS at a crossroads. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; (2024). Available at: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2024-unaids-globa....
-
- Funderburg NT, Huang SSY, Cohen C, Ailstock K, Cummings M, Lee JC, et al. Changes to inflammatory markers during 5 years of viral suppression and during viral blips in people with HIV initiating different integrase inhibitor based regimens. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1488799. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1488799 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

