Vascular-related cone-beam computed tomographic findings in healthy and medically compromised patients: A study based on self-reported medical history data
- PMID: 40607072
- PMCID: PMC12210113
- DOI: 10.5624/isd.20250029
Vascular-related cone-beam computed tomographic findings in healthy and medically compromised patients: A study based on self-reported medical history data
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the correlation between incidental vascular calcification-like imaging findings and self-reported medical data, as well as to assess the relationship between reported predisposing factors and imaging findings using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) data.
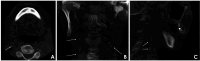
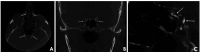
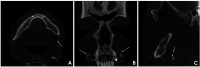
Materials and methods: A total of 391 CBCT scans from 188 males and 203 females were anonymously analyzed for the presence of extra- and intra-cranial carotid artery calcifications (ECAC and ICAC, respectively) and signs of Mönckeberg medial sclerosis (MMS). The patients were categorized into 4 groups based on their self-reported medical histories. Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the data, which were subsequently validated through simple univariate logistic regression analysis.
Results: Among the 391 CBCT scans reviewed, 23.27% exhibited ECAC, 42.71% demonstrated ICAC, and 1.8% showed MMS. Statistical analysis revealed a significant correlation (P<0.05) between both ECAC and ICAC and self-reported predisposing factors-including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus, and sleep apnea/chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-with notable differences among the study categories (P<0.05). In addition, a strong correlation (P<0.001) was found between the presence of ECAC, ICAC, and MMS and increasing age. Men were significantly more susceptible to ECAC than women (P<0.05).
Conclusion: These findings underscore the importance of a thorough pre-treatment medical history assessment in dental patients, particularly when vascular calcification-like signs are observed on CBCT imaging.
Keywords: Carotid Artery, External; Carotid Artery, Internal; Cone-Beam Computed Tomography; Monckeberg Medial Calcific Sclerosis.
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
Figures
References
-
- Damaskos S, da Silveira HL, Berkhout EW. Severity and presence of atherosclerosis signs within the segments of internal carotid artery: CBCT’s contribution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2016;122:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Bentzon JF, Otsuka F, Virmani R, Falk E. Mechanisms of plaque formation and rupture. Circ Res. 2014;114:1852–1866. - PubMed
-
- Ibañez B, Badimon JJ, Garcia MJ. Diagnosis of atherosclerosis by imaging. Am J Med. 2009;122(1 Suppl):S15–S25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

