Nanoplasmonics biosensors: At the frontiers of biomedical diagnostics
- PMID: 40607139
- PMCID: PMC12220822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2024.117973
Nanoplasmonics biosensors: At the frontiers of biomedical diagnostics
Abstract
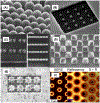
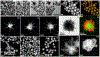
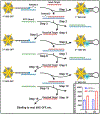
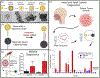
This article presents an overview of various nanoplasmonics biosensors and their diverse applications, focusing on recent developments in our laboratory. We describe the versatility and effectiveness of different plasmonics-active platforms, ranging from solid substrates to adaptable nanoparticles like gold nanostars and nanorattles. The "Inverse Molecular Sentinel" (iMS) biosensing technology uses surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) to detect nucleotide biomarkers associated with diseases ranging from acute infections to several types of cancer. We have also developed SERS-based nanochip systems capable of detecting DNA targets related to infectious disease biomarkers such as HIV, malaria, and dengue, promising advancements in global health diagnostics. Further, nanorattle-based biosensors are designed as "lab-in-a-stick" devices for rapid head and neck cancer diagnosis. Other technologies include plasmonics-enhanced lateral flow immunoassay systems, smartphone-based biosensing, and implantable biosensors or "smart tattoo" systems. These nanoplasmonics biosensors open new frontiers to rapid, simple, and effective detection systems for biomedical diagnostics.
Keywords: Biosensors; Cancer biomarkers; Global health; Liquid biopsy; Nanoplasmonics; Point-of-care; Raman; SERS.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Rapid molecular tests for tuberculosis and tuberculosis drug resistance: a qualitative evidence synthesis of recipient and provider views.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 26;4(4):CD014877. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014877.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35470432 Free PMC article.
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeanmaire DL, Van Duyne RP, Surface Raman spectroelectrochemistry: Part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem 84 (1977) 1.
-
- Albrecht MG, Creighton JA, Anomalously intense Raman spectra of pyridine at a silver electrode, J. Am. Chem. Soc 99 (1977) 5215.
-
- Moskovits M, Surface-enhanced spectroscopy, Rev. Mod. Phys 57 (1985) 783.
-
- Wokaun A, Gordon JP, Liao PF, Radiation damping in surface-enhanced Raman scattering, Phys. Rev. Lett 48 (1982) 957.
-
- Schatz GC, Theoretical studies of surface enhanced Raman scattering, Accounts of Chemical Research 17 (1984) 370.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
