From pixels to planning: scale-free active inference
- PMID: 40607319
- PMCID: PMC12217590
- DOI: 10.3389/fnetp.2025.1521963
From pixels to planning: scale-free active inference
Abstract
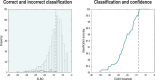
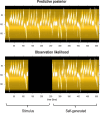
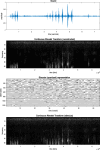
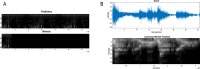
This paper describes a discrete state-space model and accompanying methods for generative modeling. This model generalizes partially observed Markov decision processes to include paths as latent variables, rendering it suitable for active inference and learning in a dynamic setting. Specifically, we consider deep or hierarchical forms using the renormalization group. The ensuing renormalizing generative models (RGM) can be regarded as discrete homologs of deep convolutional neural networks or continuous state-space models in generalized coordinates of motion. By construction, these scale-invariant models can be used to learn compositionality over space and time, furnishing models of paths or orbits: that is, events of increasing temporal depth and itinerancy. This technical note illustrates the automatic discovery, learning, and deployment of RGMs using a series of applications. We start with image classification and then consider the compression and generation of movies and music. Finally, we apply the same variational principles to the learning of Atari-like games.
Keywords: Bayesian model selection; active inference; active learning; compression; network-physiology; renormalization group; structure learning.
Copyright © 2025 Friston, Heins, Verbelen, Da Costa, Salvatori, Markovic, Tschantz, Koudahl, Buckley and Parr.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors KF, CH, TV, LC, TS DM, AT, MK and CB were employed by company VERSES Research Lab. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors KF, DM and TP declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures



















Similar articles
-
Psychological therapies for panic disorder with or without agoraphobia in adults: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 13;4(4):CD011004. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011004.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27071857 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Using Generative Adversarial Networks for Glaucoma Detection: Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Sep 21;23(9):e27414. doi: 10.2196/27414. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34236992 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that influence parents' and informal caregivers' views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 27;10(10):CD013265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013265.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34706066 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging a foundation model zoo for cell similarity search in oncological microscopy across devices.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 18;15:1480384. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1480384. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40606969 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
How do inner screens enable imaginative experience? Applying the free-energy principle directly to the study of conscious experience.Neurosci Conscious. 2025 Apr 22;2025(1):niaf009. doi: 10.1093/nc/niaf009. eCollection 2025. Neurosci Conscious. 2025. PMID: 40265192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attias H. (2003). Planning by probabilistic inference. Proc. 9th Int. Workshop Artif. Intell. Statistics.
-
- Ay N., Bertschinger N., Der R., Guttler F., Olbrich E. (2008). Predictive information and explorative behavior of autonomous robots. Eur. Phys. J. B 63, 329–339. 10.1140/epjb/e2008-00175-0 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

