Influence of extracorporeal shockwaves on macrophage polarization in a 3D collagen matrix
- PMID: 40607331
- PMCID: PMC12213261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.06.003
Influence of extracorporeal shockwaves on macrophage polarization in a 3D collagen matrix
Abstract
Introduction: The host's immune response determines the success of guided tissue regeneration. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) has been shown to reduce inflammation and improve wound healing. Nevertheless, its impact on macrophage polarization, as the first line of host defense, has not yet been elucidated. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effect of ESWT on macrophage polarization in a 3D collagen matrix model.
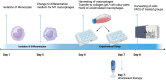
Methods: Macrophages were isolated from human donor blood and differentiated into M1 macrophages. The cells were seeded into a collagen gel, and macrophages treated with ESWT (500 impulses, energy flux density 0.12 mJ/mm2) (+ESWT) were compared to non-treated cells (-ESWT). Furthermore, macrophages treated with 20 ng/μl IL-4 and 50 ng/μl M-CSF for M2-polarization in the gel (1.) or on a 6-well cell culture plate with Upcell™ surface (2.) as well as M1 macrophages cultured on a conventional cell culture dish (3.) served as reference cultures. Flow cytometry assessed polarization into M2 macrophages by measuring the expression of CD209, CD86, CD200R, and CD163.
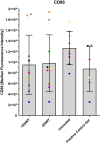
Results: Flow cytometry revealed no significant differences between the ESWT-treated (+ESWT) and untreated (-ESWT) macrophages for any of the markers. However, macrophages cultured in collagen gel (3) exhibited significantly higher CD200R expression rates than the other groups.
Conclusions: The lack of significant differences in macrophage polarization following ESWT in this 3D model may be attributed to the absence of cell-cell interactions and other tissue structures that are present in vivo. Since the culturing environment significantly affected the expression of M2-polarization markers, with a significantly higher expression in collagen gel compared to cell culture plates, future studies should incorporate more complex co-culture systems or in vivo models to better simulate the clinical environment. Clinical evidence suggests that ESWT can effectively promote tissue healing and regeneration, indicating that the observed results may reflect limitations in the chosen model or cell type rather than the therapy itself, warranting further investigation.
Keywords: 3D model; Collagen matrix; ESWT; Extracorporeal shockwave therapy; Macrophage polarization.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were funded by the supporting societies.
Figures




References
-
- Kammerer P.W., Scholz M., Baudisch M., Liese J., Wegner K., Frerich B., et al. Guided bone regeneration using collagen scaffolds, growth factors, and periodontal ligament stem cells for treatment of peri-implant bone defects in vivo. Stem Cell Int. 2017;2017 doi: 10.1155/2017/3548435. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

