Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma hyorhinis and virulence evaluation of its field isolates
- PMID: 40607351
- PMCID: PMC12213342
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1542992
Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma hyorhinis and virulence evaluation of its field isolates
Abstract
Introduction: As a prevalent swine pathogen worldwide, Mycoplasma hyorhinis (M. hyorhinis, Mhr) is associated with various diseases, including multiple serositis, pneumonia, arthritis, and otitis media. It is also linked to the porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC).
Methods: M. hyorhinis prevalence in 2022 Chinese lung samples was assessed by species-specific PCR, followed by isolation and purification of field strains, followed by genetic characterization via multilocus sequence typing (MLST). Pathogenicity evaluation of three isolates (ZZ-1, GD-1 and AH-1) was evaluated using controlled piglet infection trials.
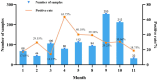
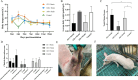
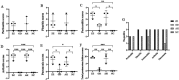
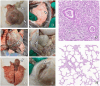
Results: Mhr detection in clinical lung samples showed 31.77% prevalence. Three isolates (ZZ-1/ST166, GD-1/ST167, AH-1/ST144) were characterized by MLST. Piglet infection trials confirmed Mhr-induced polyserositis, pneumonia, and arthritis, with strain-dependent virulence variation observed.
Discussion: This study confirms M. hyorhinis as a high-prevalence pathogen (31.77%) in Chinese swine herds. Animal infection models demonstrated virulence variation among different Mhr strains. These findings contribute to identifying and assessing the threats posed by different strains to pig health, guiding the development of clinical prevention and control strategies.
Keywords: Mycoplasma hyorhinis; identification; infection; isolation; positivity rate.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Yang, Duan, Qian, Ma, Jia, Huo, Dong, Chen and Tan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

