Exploring the antineoplastic potential of α-mangostin in breast cancer
- PMID: 40608162
- PMCID: PMC12229438
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-025-00528-5
Exploring the antineoplastic potential of α-mangostin in breast cancer
Abstract
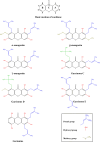
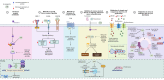
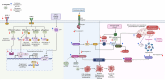
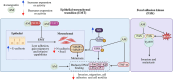
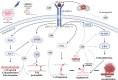
Among women, breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer-related mortality globally. Despite improvements in early detection and diagnosis, some risk factors have been on the rise, including the decline in birth rate, the use of oral contraceptives, and the escalation in alcohol consumption and obesity. Thus, there is an imperative urgent need to expand accessible prevention and treatment options for breast cancer. Regarding these tumors, several natural compounds have shown efficacy in slowing or preventing their progression, offering a promising therapeutic alternative. Among these, α-mangostin, a xanthone derived from mangosteen, has demonstrated promising antitumor effects against different malignancies, particularly breast cancer. The mechanisms involved in α-mangostin´s therapeutic effects include downregulation of oncogenic ion channels, modulation of cell cycle progression, suppression of oncogene expression, and interference with steroid and growth factor receptors signaling. This review thoroughly explores these mechanisms, as well as updates information on α-mangostin chemical structure and its potential as a coadjuvant to conventional breast cancer therapies. Furthermore, we provide scientifically supported insights for the development of clinically applicable α-mangostin-based treatments, highlighting the robust body of evidence supporting its cancer-fighting properties, despite the absence of clinical studies to date.
Keywords: Antineoplastic effects; Breast cancer; Garcinia mangostana; Xanthone; α-Mangostin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Informed consent: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. 10.3322/caac.21834. - PubMed
-
- Bissoli I, Muscari C. Doxorubicin and α-mangostin oppositely affect luminal breast cancer cell stemness evaluated by a new retinaldehyde-dependent ALDH assay in MCF-7 tumor spheroids. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;124:109927. 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109927. - PubMed
-
- Lara-Sotelo G, Díaz L, García-Becerra R, Avila E, Prado-García H, Morales-Guadarrama G, et al. α-mangostin synergizes the antineoplastic effects of 5-fluorouracil allowing a significant dose reduction in breast cancer cells. Processes. 2021;9(3):458. 10.3390/pr9030458.
-
- Vargas-Castro R, Garcia-Becerra R, Diaz L, Avila E, Ordaz-Rosado D, Bernadez-Vallejo SV, et al. Enhancing tamoxifen therapy with α-mangostin: synergistic antiproliferative effects on breast cancer cells and potential reduced endometrial impact. Pharmaceuticals. 2023. 10.3390/ph16111576. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alam M, Rashid S, Fatima K, Adnan M, Shafie A, Akhtar MS, et al. Biochemical features and therapeutic potential of α-mangostin: mechanism of action, medicinal values, and health benefits. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;163:114710. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114710. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

