Exploring the radiochemistry of PARP inhibitors: a new era in therapy and imaging
- PMID: 40608261
- PMCID: PMC12229409
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-025-00364-5
Exploring the radiochemistry of PARP inhibitors: a new era in therapy and imaging
Abstract
Background: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have emerged as a promising class of therapeutics, particularly in the treatment of cancers with defective DNA repair mechanisms, such as those with breast cancer genes (BRCA) mutations. Their effectiveness in cancer therapy is now well-established, but the ongoing advancements in radiochemistry are expanding their potential to combine both therapeutic and imaging capabilities. Radiolabelled PARP inhibitors, used in conjunction with positron emission tomography (PET) or single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), might enable precise imaging of PARP expression in tumours, potentially providing invaluable insights into treatment response, tumor heterogeneity, and molecular profiling.
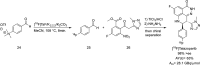
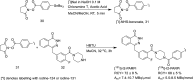
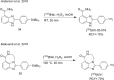
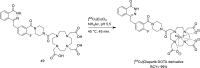
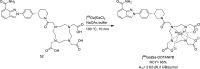
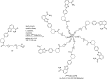
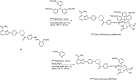
Main body: The radiochemistry of PARP inhibitors involves incorporating radioisotopes (most of all Fluorine-18) into the molecular structure of these molecules. The first strategy used to achieve this goal was the use of prosthetic groups bearing the fluorine-18. Then, the development of radioisotopologue have gained ground, followed later by the replacement with other halogens such as bromine, iodine, or astatine has taken place. Another frontier is represented by the metal radiolabelling of these inhibitors through the introduction of a chelator moiety to these molecules, thus further expanding both imaging and therapy applications.
Conclusion: Finally, emerging evidence suggest the possibility to involve PARP-related radiopharmaceuticals in theranostics approaches. Despite challenges such as the complexity of radiolabelling, regulatory hurdles, and the need for more robust clinical validation, the continued exploration of the radiochemistry of PARP inhibitors promises to revolutionize both the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, offering hope for more effective and personalized cancer care.
Keywords: Niraparib; Olaparib; PARP; PARP imaging; PARP inhibitor; PARP therapy; PARP1; Radiolabelling; Rucaparib; Talazoparib.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
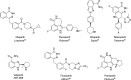
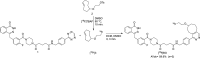


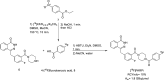


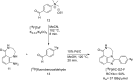
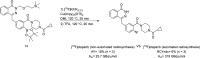
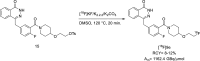

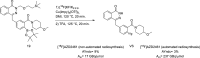










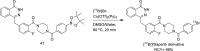
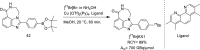
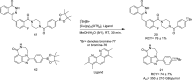
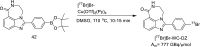
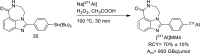
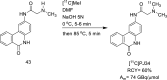


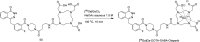
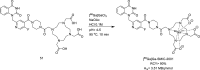

References
-
- Adam MJ, Wilbur DS. Radiohalogens for imaging and therapy. Chem Soc Rev. 2005;34:153–63. - PubMed
-
- Andersen TL, Friis SD, Audrain H, Nordeman P, Antoni G, Skrydstrup T. Efficient 11C-carbonylation of isolated aryl palladium complexes for PET: application to challenging radiopharmaceutical synthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:1548–55. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
